


 In the times when the world is fighting against the Coronavirus pandemic and looks forward to creating vaccine, the increase of public trust toward the vaccination has a paramount importance. Throughout the centuries, the vaccination has helped the mankind produce immunity against such diseases as measles, rubella, mumps, tuberculosis, tetanus, etc. However, since the day of the invention of vaccine, there have been some people who have been opposing the fighting against diseases through this method due the different reasons.
In the times when the world is fighting against the Coronavirus pandemic and looks forward to creating vaccine, the increase of public trust toward the vaccination has a paramount importance. Throughout the centuries, the vaccination has helped the mankind produce immunity against such diseases as measles, rubella, mumps, tuberculosis, tetanus, etc. However, since the day of the invention of vaccine, there have been some people who have been opposing the fighting against diseases through this method due the different reasons.
In different times, different methods for increasing the public trust toward the vaccination have been used. Usually, for this purpose, popular and authoritative figures got vaccinated publicly. There is a historical evidence that in 1772,when there was a Black Death epidemic in Kartli, Erekle II got his son, Iulon vaccinated publicly after which the public trusted the innovation and started the vaccination of their children. In 1956, at The Ed Sullivan’s Show, Elvis Presley received the Polio vaccine publicly after which the numbers of vaccination in the US increased from 0.6% to 80%.
In the end of XX and the beginning of XXI century, the anti-vaccination movements achieved unprecedented scales, which can, on the one hand, be explained by the development of information sources, which has accelerated the exchange of information among people. However, nowadays, these movements are directly related to the name of British ex-physician, Andrew Wakefield, who was later deprived of the medical qualification in the UK.
On 28 Ferbuary 1998, Wakefield together with his co-authors published a work in the scientific journal The Lancet. The publication included the study of twelve children with autism based on which he concluded that that there was a link between the development of autism in children and MMR vaccine. Although, none of the similar researches carried out worldwide proved the links between autism and vaccination, Wakefield’s research became viral in media and among scientific circles after which the anti-vaccination campaigns became more active. As a result, shortly, several outbreaks of measles were monitored worldwide. In 2004, Wakefield’s research attracted the public interest once again following the publication of an article by a journalist, Brian Deer in The Sunday Times. The article argued that the parents of the twelve children involved in Wakefield’s study were hired by the British lawyer who was preparing a lawsuit against MMR manufacturers at the same time. Also, The Sunday Times reported that Wakefield received more than 400,000 pounds from lawyers for the same research. After the publication of the articles in The Sunday Times, The British General Medical Council (GMC) carried out an investigation based on which he was barred from practicing medicine in the UK. Also, his article was removed from The Lancet publications. However, this did not interfere with the already flared-up anti-vaccination campaign worldwide, which is active until today.
Recently, the footprints of Russian propaganda in the enhancement of anti-vax movements have also been evident.
In 2018, the Professor at George Washington University, David Broniatowski together with his co-authors published a research, in which it is argued that in the social media, thousands of Russian accounts spread the disinformation about vaccination and amplified the anti-vaccination sentiments. The researchers collected and analyzed more than 2 million tweets, based on which they concluded that the Russian trolls were more likely to post about vaccination than the usual users. As it is mentioned in their research, Russian propaganda used the topic of vaccination to sow distrust toward the healthcare systems and the government, polarization and chaos in the US society.
It is notable that Russian troll-accounts spread the pro-vaccination as well as anti-vaccination information. However, the greatest share of the messages was on the anti-vax information (see Graphic 1). For instance, here are some tweets by Russian accounts: “#vaccines are a parent’s choice. Choice of a color of a little coffin #VaccinateUS.”; “Did you know there was a secret government database of #vaccine-damaged children? #VaccinateUS.”; “Do you still treat your kids with leaves? No? And why don’t you #vaccinate them? Its medicine! #VaccinateUS”. According to the research, through spreading such equivocal messages, Russian propaganda attempted to create an illusion of an existing debate related to vaccination in the society, which increased the polarization of the American public.
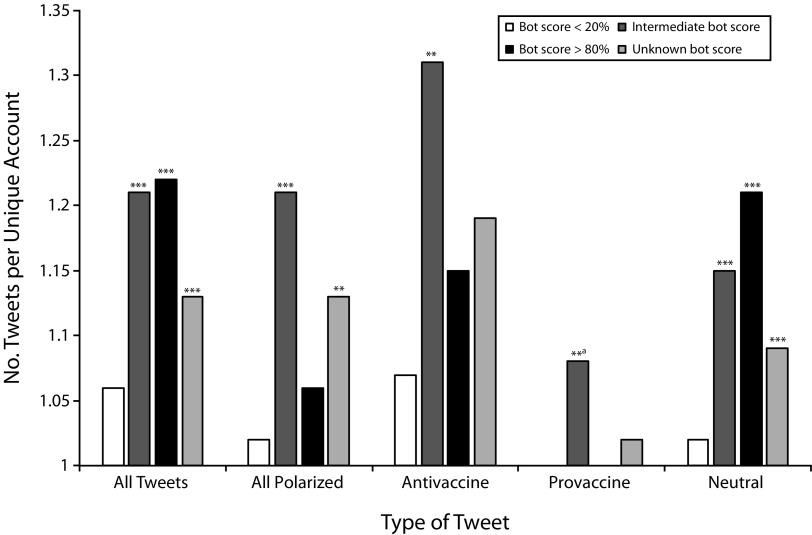
Graphic 1. Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6137759/
It is also significant that this is not the first case when Russia launched an informational warfare against the US healthcare system. The Soviet government also used disinformation against US, which is best revealed in the so-called “Operation Infection” – the spread of disinformation worldwide that the AIDS virus was created by US at the Fort Detrick Research Center. [1] According to the Soviet propaganda narrative, it was an attempt of Pentagon to create a biological weapon which was successfully tested in Latin America, Africa and Pakistan. The detailed information about the “Operation Infection” can be found in IDFI’s article.
The Russian disinformation related to public health and vaccines is active until now and it covers not only US but the whole world, especially the countries that appear to be the targets of Russia’ strategic interests. In that sense, Georgia is not an exception.
Anti-Vaxers and Georgia
In Georgia, the anti-vaccination campaign is not as large-scale as in US and Europe. However, Russia’s role in the spread of conspiracy theories in this direction is also evident here. For instance, in 2019, in the issue of 25 February – 3 March of the newspaper “Asaval-Dasavali”, an interview with the head of the Georgian bureau of Veterans Today, Jeffrey Silverman was published, in which he argues that the H1N1 and measles vaccines are not created in Europe but in Georgia, at the US Lugar Laboratory.

Jeffrey Silverman
In general, the Lugar Laboratory has been a target of Russian disinformation for years and the conspiracy theories about it are being spread even today. Russian propaganda has been arguing for years that US used the laboratory in Georgia for spreading the biological weapon. The interview with Jeffrey Silverman published in “Asaval-Dasavali” is also a part of this disinformation. Silveram himself is an American journalist living in Georgia who is one of the sources related to Lugar Laboratory disinformation of Russian and pro-Russia media outlets.
“If the vaccination is necessary, I will get the vaccine produced in Russia not in US or Lugar Laboratory! The thing is that much more people died from these vaccines than from flu” – Jeffrey Silverman, “Asaval-Dasavali”, 25 February – 3 March 2019.
“Here [at Lugar’s Laboratory] are the biological agents, especially dangerous substances. They can be used as a weapon. You remember that, a few years ago, people in Georgia and South of Russia died from Swine Flu. This was not coincidental” – Jeffrey Silverman, “Asaval-Dasavali”, Rossia 24, Vesti Nedeli, 16 September.
Jeffrey Silverman’s similar announcements were published by an online media “Georgia and the World” (geworld.ge) already in 2015:
There are the rooms in the laboratory in which the corpses are being burnt. As for the experiments on humans, they are carried out through different types of viruses and vaccines. These experimental vaccines, that have been transferred to the Ministry of Health of Georgia, are very doubtful as they are donated by the Defense Department of US. Bear in mind that nothing is for free in this life except for the bait placed in trap.”
In fact, the Lugar Laboratory does not produce vaccines or any other types of medicine. Therefore, Silverman’s accusations are total disinformation. The vaccines for H1N1 and measles are imported to Georgian from US and EU. These vaccines are studied and qualified by the World Health Organization (WHO) and they are being used not only by Georgia but by Russia as well.
It is notable that regardless of the disinformation spread by Russia for years, according to the 2018 statistics of the National Center for Disease Control and Public Health of Georgia, the numbers of immunization in Georgia are quite high and improve annually. Currently, the 12 vaccines for the infectious diseases are available in the country: tuberculosis, hepatitis B, diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus, poliomyelitis, measles, mumps, Hib (Haemophilus influenzae), Rota virus, pneumococcus infection. The immunization coverage of 2018 is significantly higher than that of the previous years. There is a significant increase in the coverage of the following vaccines: Hep B0 – 93.6% in 2017 and 96.4% in 2018, MMR1 – 95.5% in 2017 and 98.7% in 2018, MMR2 – 89.9% in 2017 and 95.7% in 2018, Td – 76% in 2017 and 88.3% in 2018 (Graphic 2).
Graphic 2: The Scale of Immunization (%), Georgia, 2018
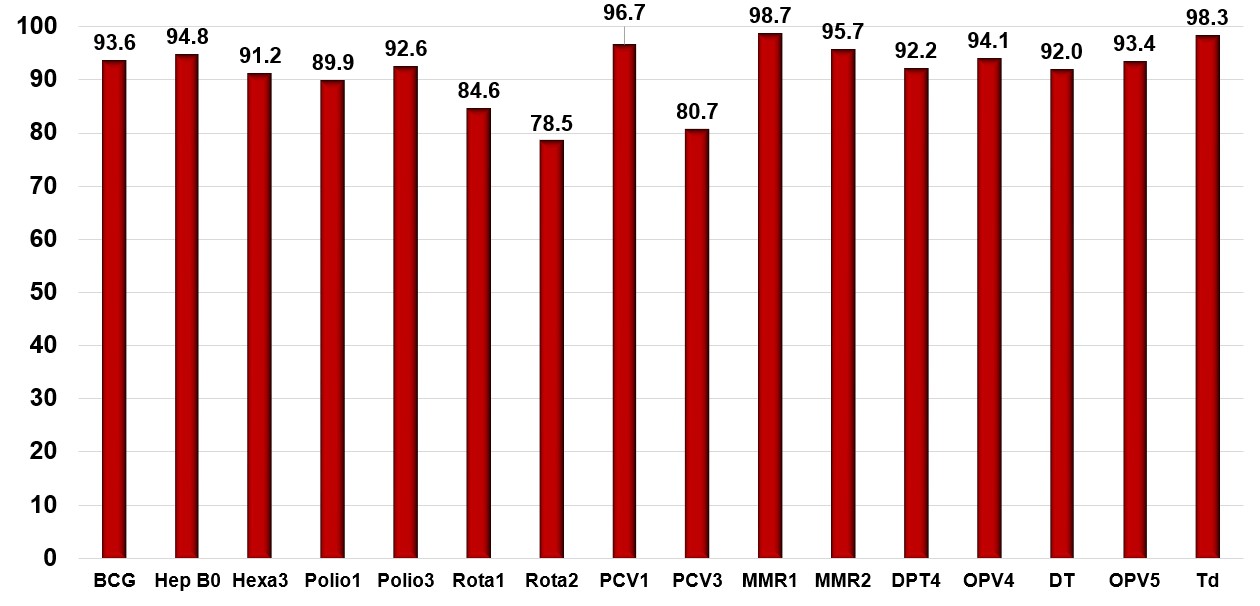
Source:The National Center for Disease Control and Public Health of Georgia
Also, there is an increase in the coverage of vaccination against measles among the children younger than 1 year and in 2018, the highest number was shown in this direction (Graphic 3).
Graphic 3:The Coverage of the Measles Vaccination among Children under 1 (%)
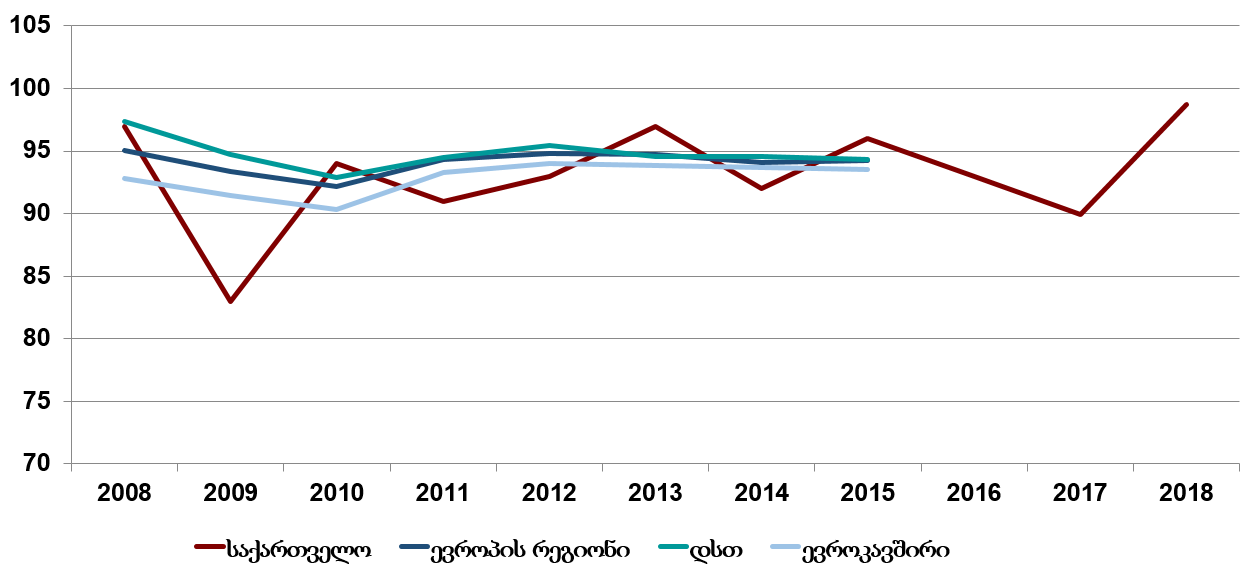
Source: the database “Health for Eveyone” of WHO, National Center for Disease Control and Public Health of Georgia.
Regardless of the positive statistics of immunization in Georgia, Russian disinformation related to vaccines deserves particular attention as long as it can significantly affect this positive tendency. The Russian disinformation campaign, aimed directly against the healthcare systems of different countries bears significant risks not only politically but medically as well. On the one hand, in this way, Russia attempts to sow distrust, polarization and chaos in foreign countries, which bears political risks for public. On the other hand, the increased mistrust toward the healthcare organs and medicine in the society can endanger the health of the general public, which was proved by the increased cases of measles in US after the activization of anti-vaccination campaigns.
Amid the Coronavirus global crisis, an increased public attention is directed toward the information related to healthcare issues for which the disinformation related to similar topics can affect larger audience and may further enhance the mistrust toward vaccines and public healthcare in general in the society. Therefore, in these times of crisis, it is important for Georgia to have a comprehensive strategy for countering such disinformation in order to avoid the increase of mistrust toward healthcare systems and decision-makers in the society. The damage caused by the disinformation is real as long as it can significantly endanger the health of the citizens and negatively affect the positive tendencies the country has in terms of the public immunization.
____
[1] Schoen, Fletcher; Lamb, Christopher J. Deception, Disinformation, and Strategic. Communications: How One Interagency Group. Made a Major Difference // Strategic Perspectives : journal. — 2012. — 1 June (vol. 11).

This material has been financed by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency, Sida. Responsibility for the content rests entirely with the creator. Sida does not necessarily share the expressed views and interpretations.