Submission of a Legislative Initiative by 30,000 Voters
An Initiative Group that consists of no less than 5 members is formed.
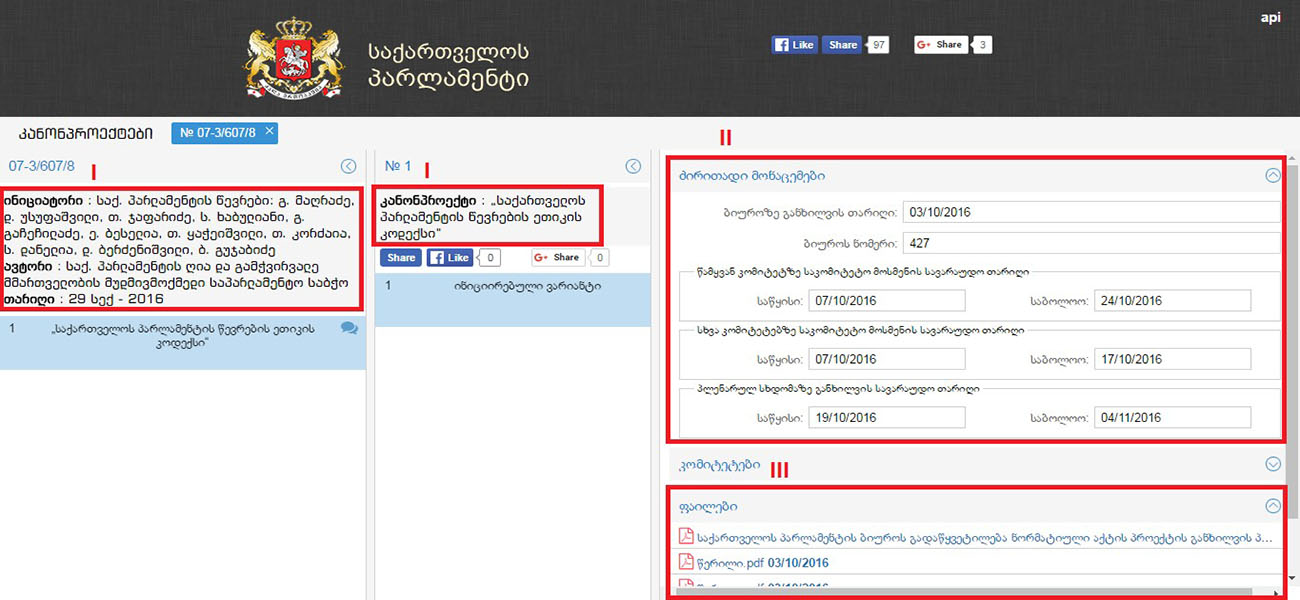
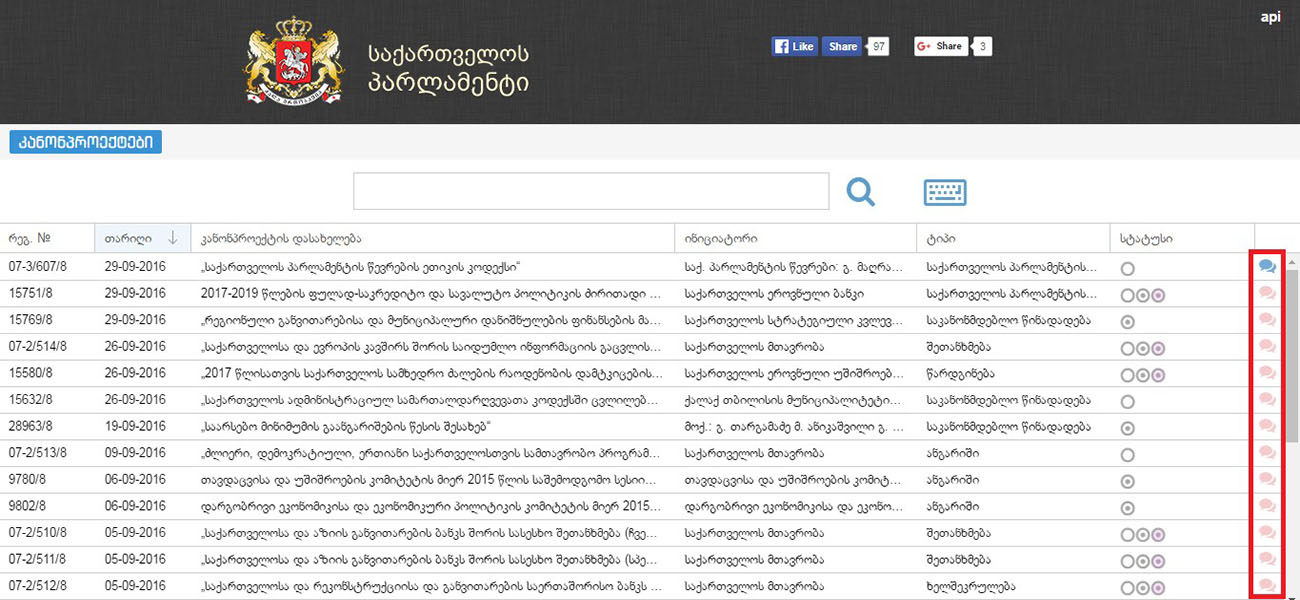
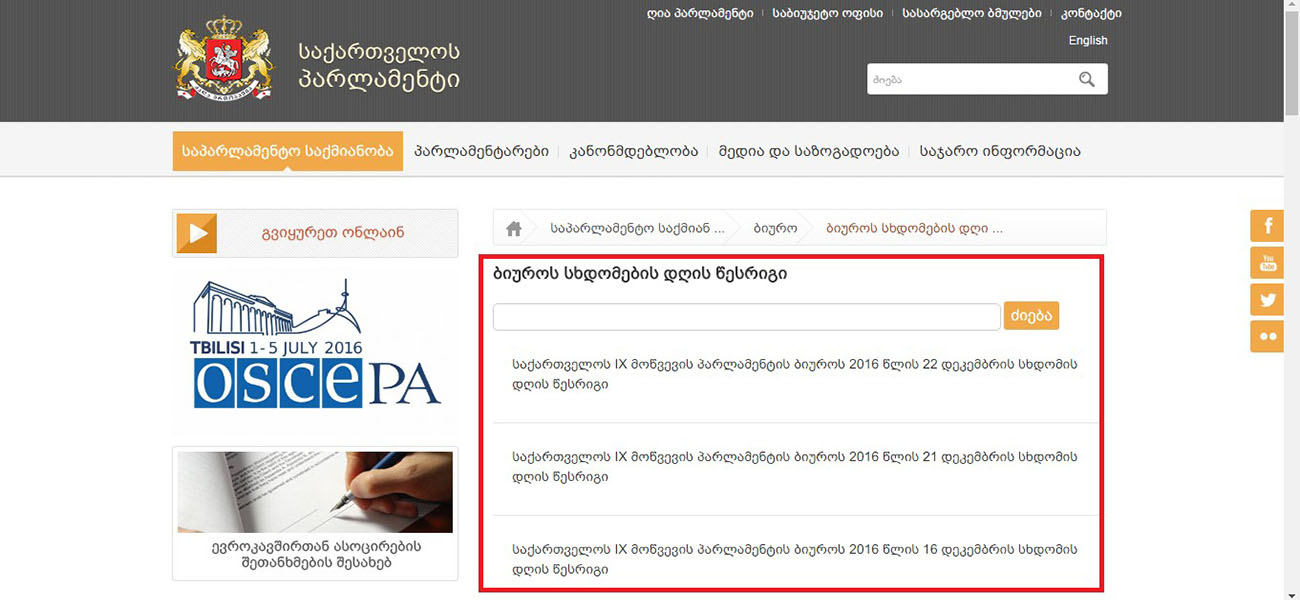
The Initiative Group addresses the Bureau of Parliament with the requrst to register the draft law. The draft law and personal data of the members of the Group accompany the Request.
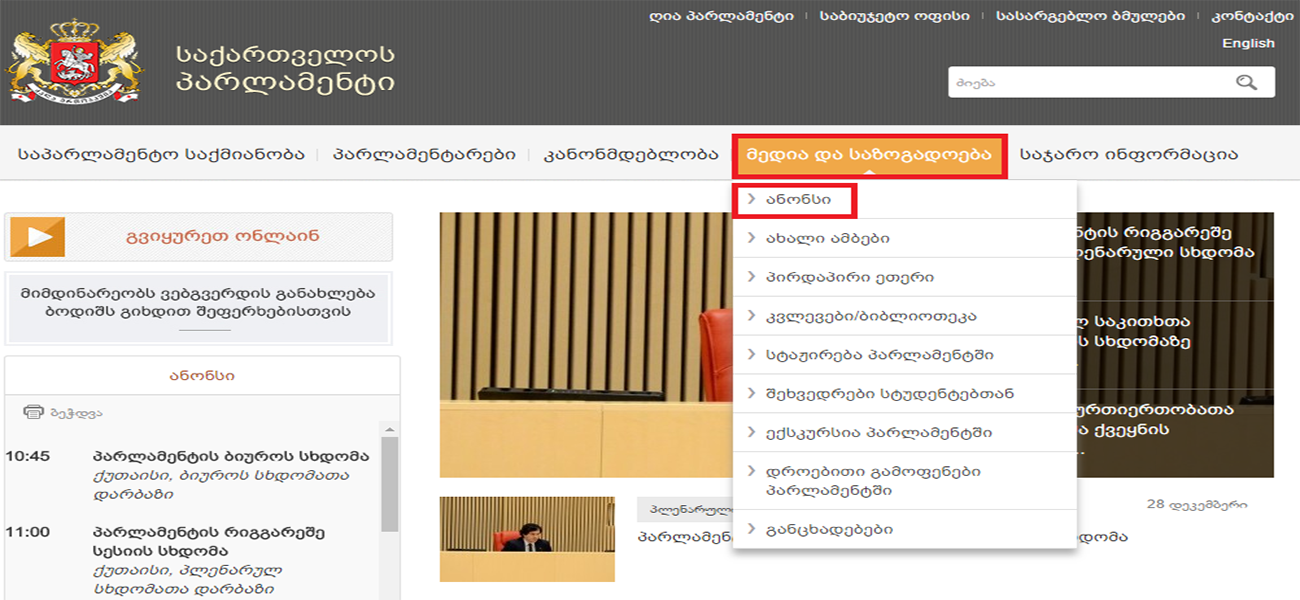
The Bureau of Parliament forwards the Request to the Committee of Procedural Issues and Rules.
In case of a positive decision on registration, the Committee of Procedural Issues and Rules gives a registration certificate to the Initiative Group.
Upon receipt of the registration certificate, the Initiative Group begins collecting signatures of supporters of the draft law.
The Initiative Group submits the signed paper to the Bureau of Parliament. The Bureau forwards the paper to the Committee of Procedural Issues and Rules.
The Committee of Procedural Issues and Rules examines the authenticity and the number of signatures (that mustl not be less than 30,000).
In case of confirmation of authenticity and required amount of signatures, the conclusion of the Committee of Procedural Issues and Rules and the draft law are submitted to the Bureau, and the list of signatures is submitted to the Organizational Department.
The draft law submitted by means of initiative of 30,000 voters is introduced to the Parliament by the member of the Initiative Group and by the representative of the Leading Committee.
Submission of a Legislative Proposal
A legislative proposal can be made by a citizen of Georgia, state bodies, local government bodies, political and public unions.
The legislative proposal shall include its reasoning, signature and address of the author.
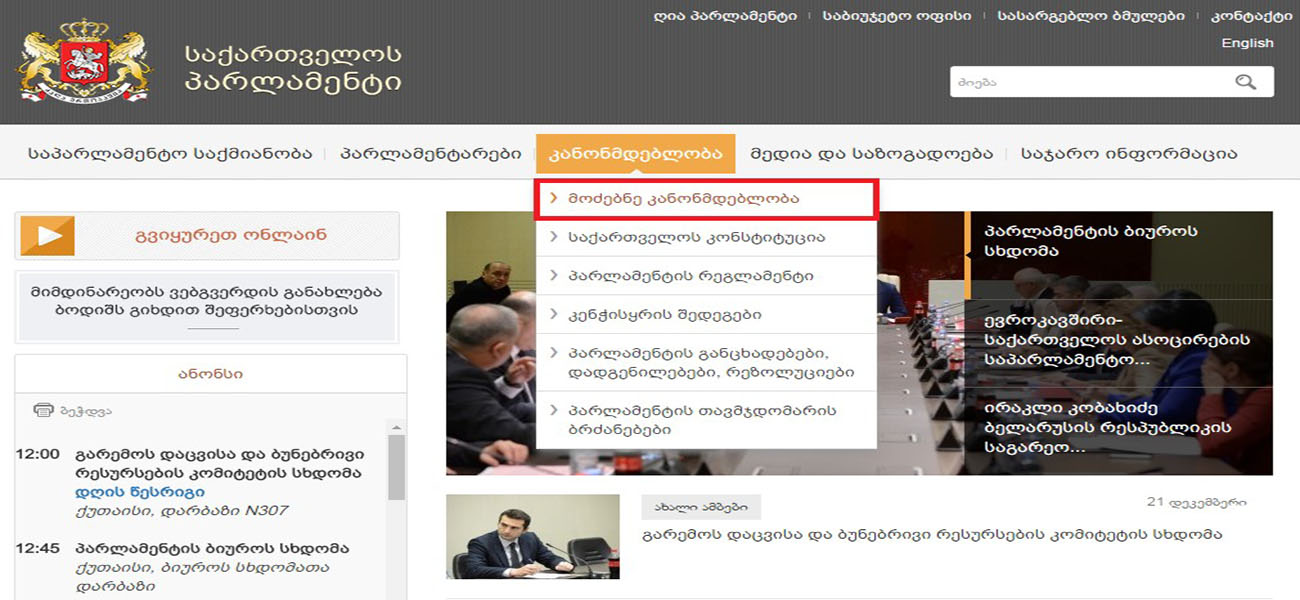
The Parliament Bureau or the Speaker defines the leading committee (the committee that shall be responsible for drafting the draft in case the legislative proposal is accepted) and submits the legislative proposal to it.
The leading committee submits to the Bureau the draft law drafted on the basis of the legislative proposal. The Bureau, for its part, includes the subbmited draft law in the agenda of the nearest parliamentary session.
 Lack of awareness of citizens is one of the main obstacles for their active participation in legislative processes.
Lack of awareness of citizens is one of the main obstacles for their active participation in legislative processes. Government should be making information related to legislative processes available. The legislative process should be derived from the interests of the population.
Government should be making information related to legislative processes available. The legislative process should be derived from the interests of the population. This module was created by the Institute for Development of Freedom of Information (IDFI) and reviews lawmaking activities and citizen participation mechanisms that are currently available through the website of the Parliament of Georgia.
This module was created by the Institute for Development of Freedom of Information (IDFI) and reviews lawmaking activities and citizen participation mechanisms that are currently available through the website of the Parliament of Georgia.