How to Use E-mail Safely
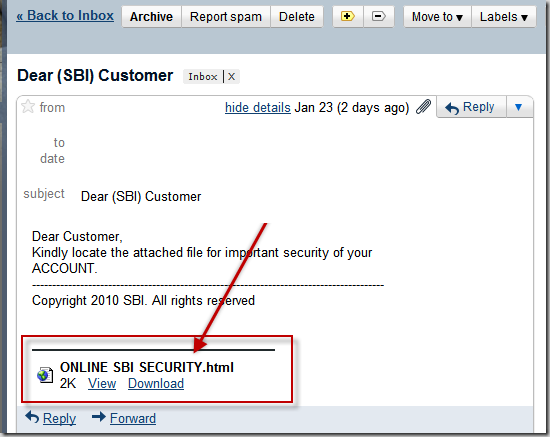
E-mail has become an integral part of modern life. Neither professional nor civic activity is possible without it. This is also the reason why email is often used for carrying out cyberattacks that range from relatively harmless spam to more serious crimes, e.g. hacking of e-mails, stealing financial information or extortion.
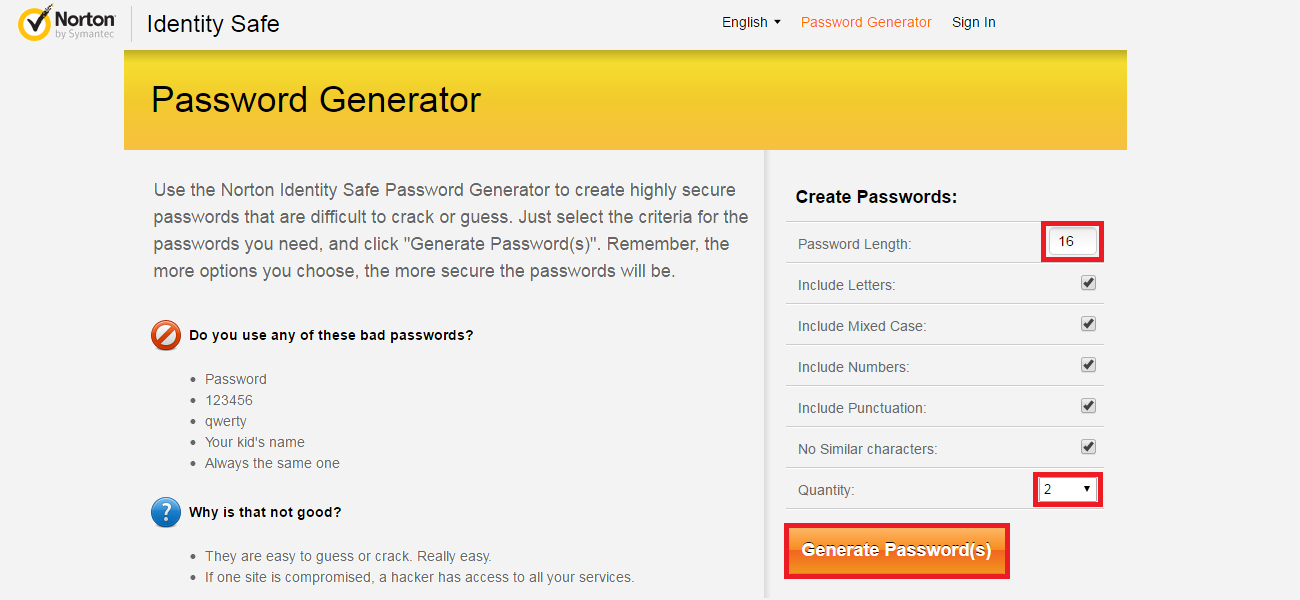
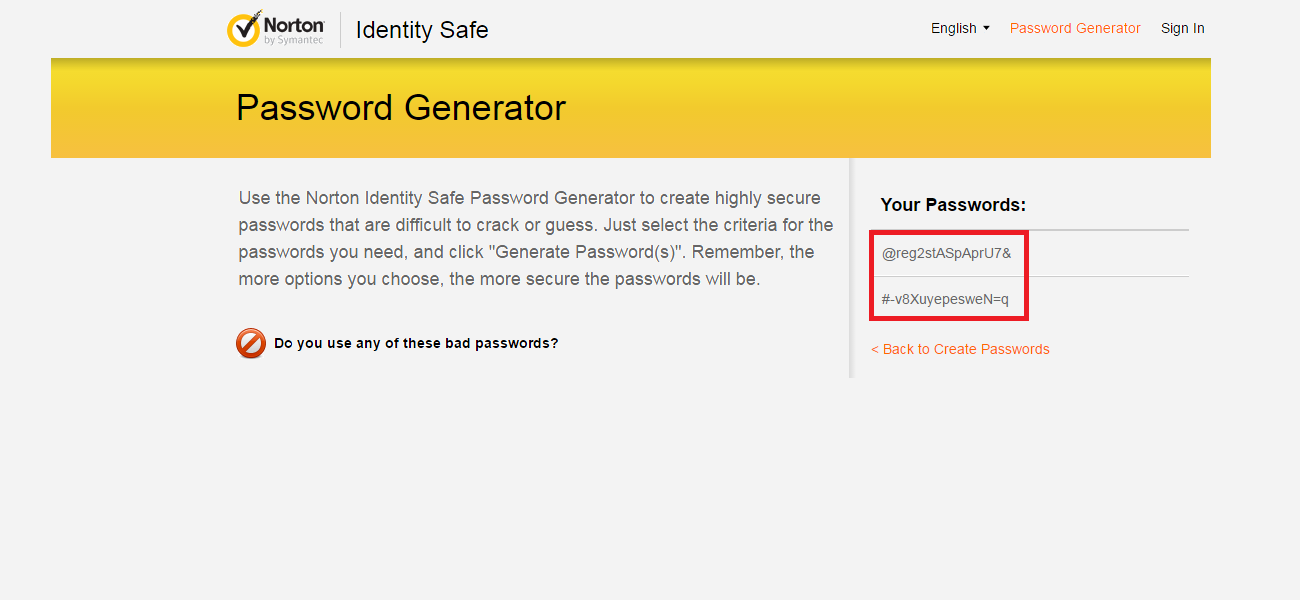
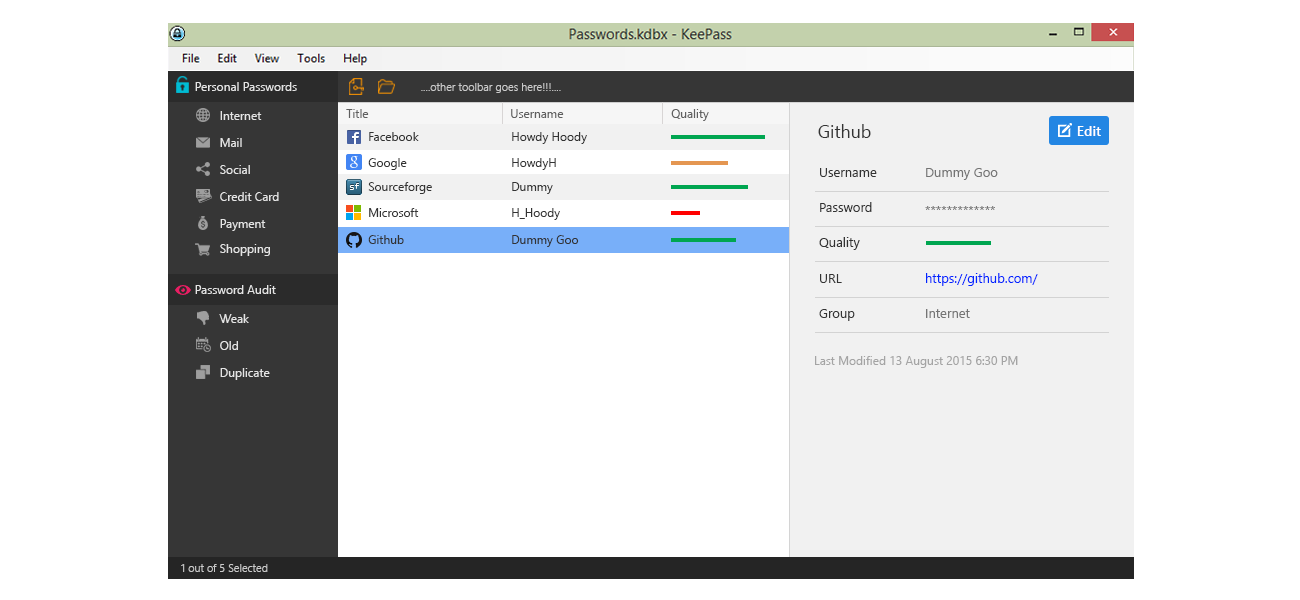
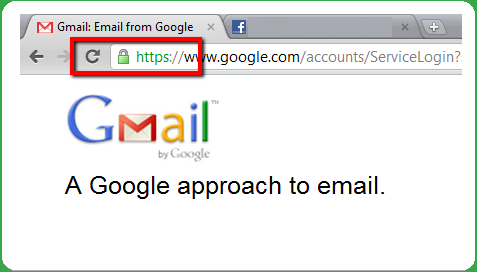
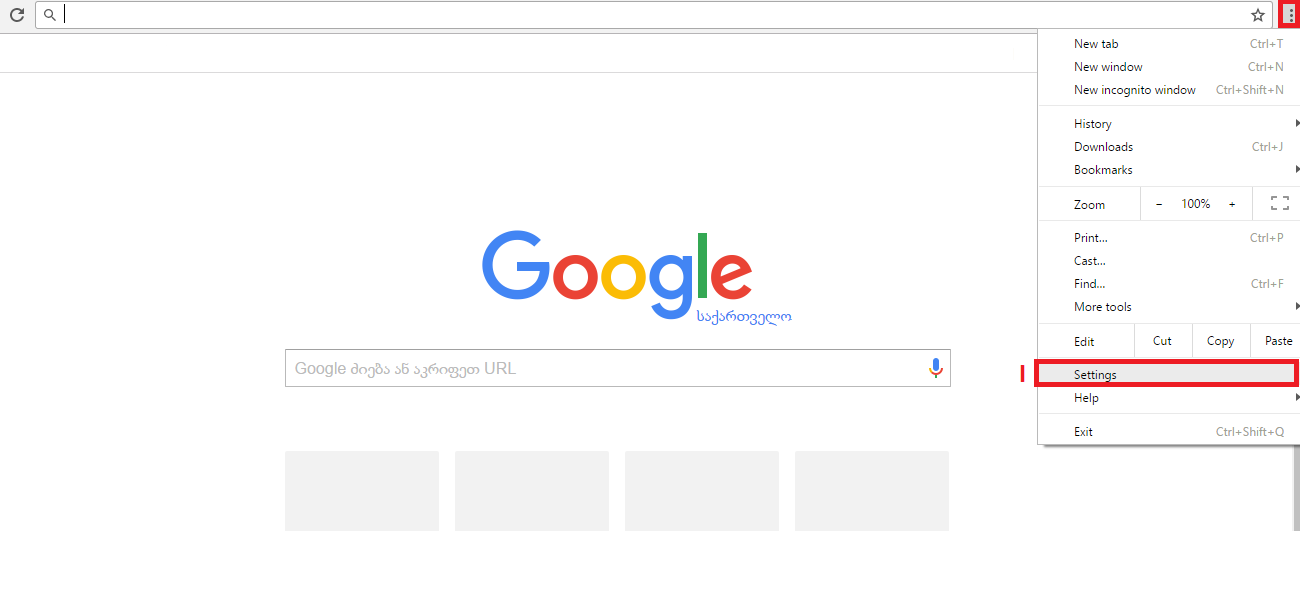
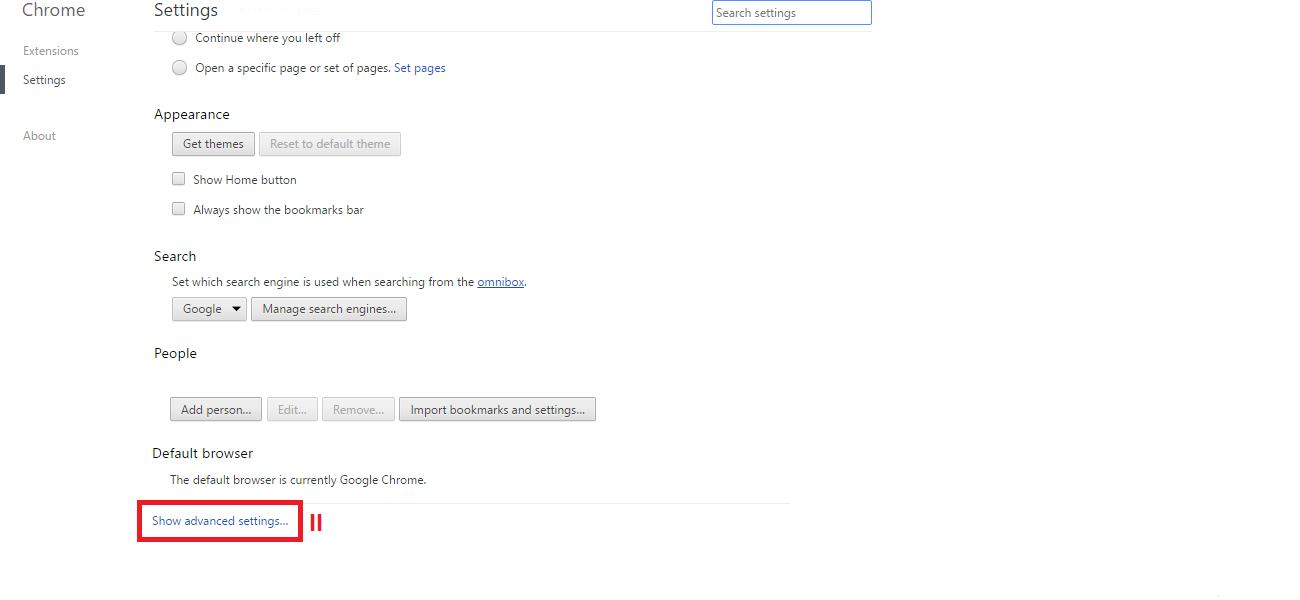
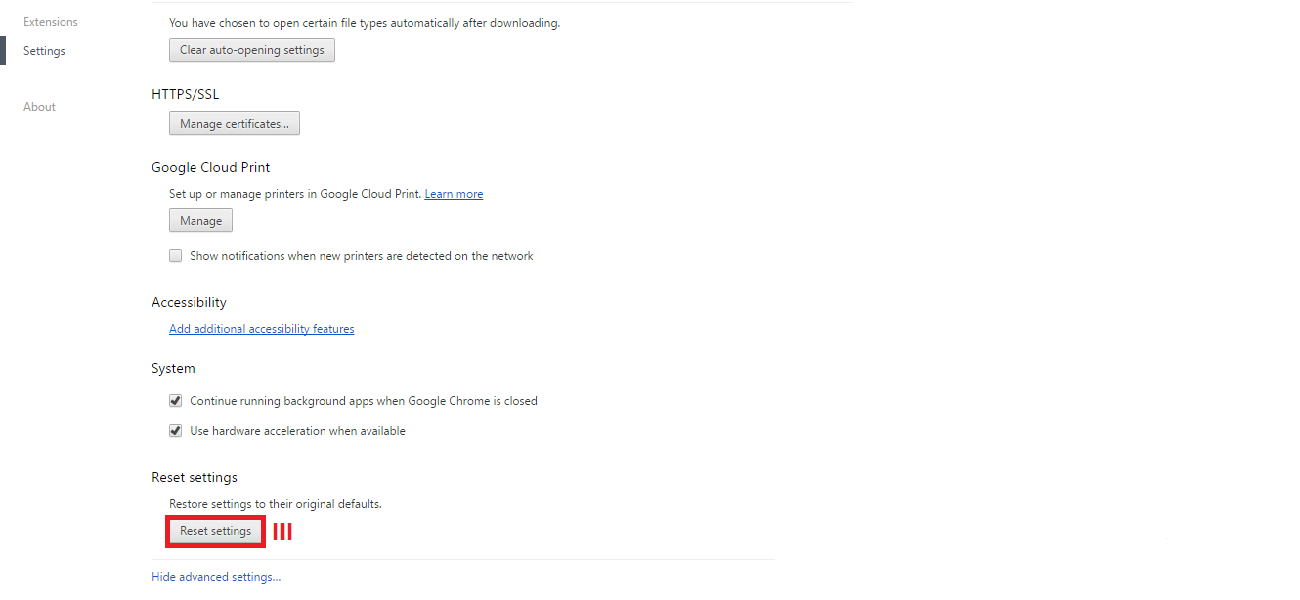
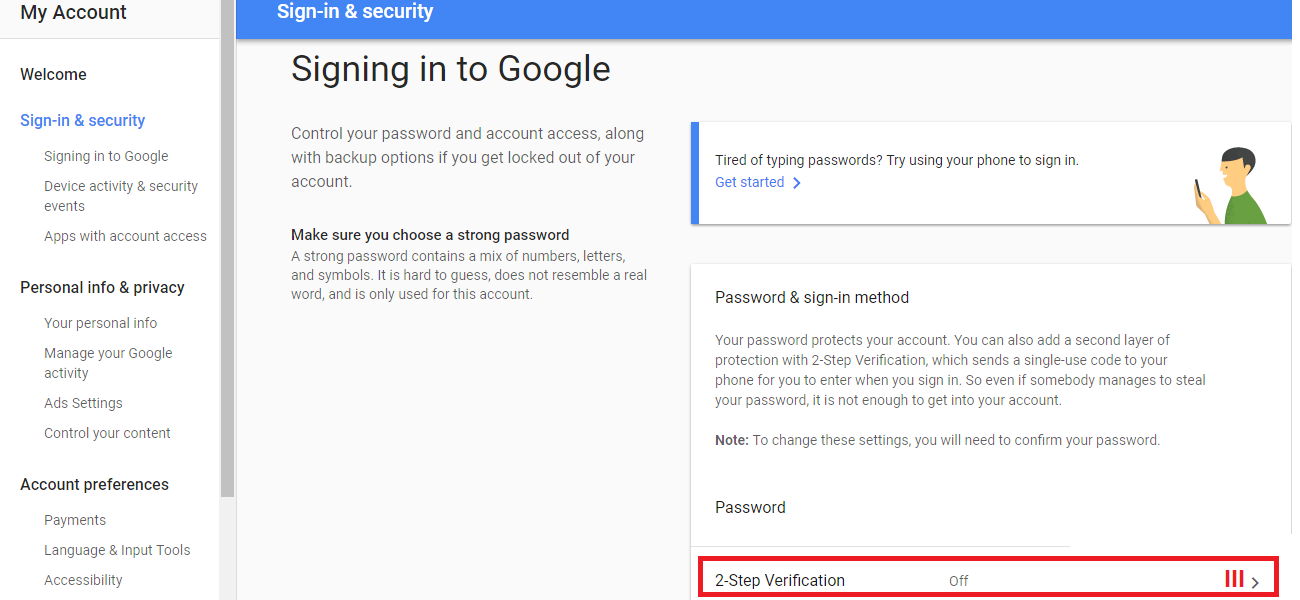
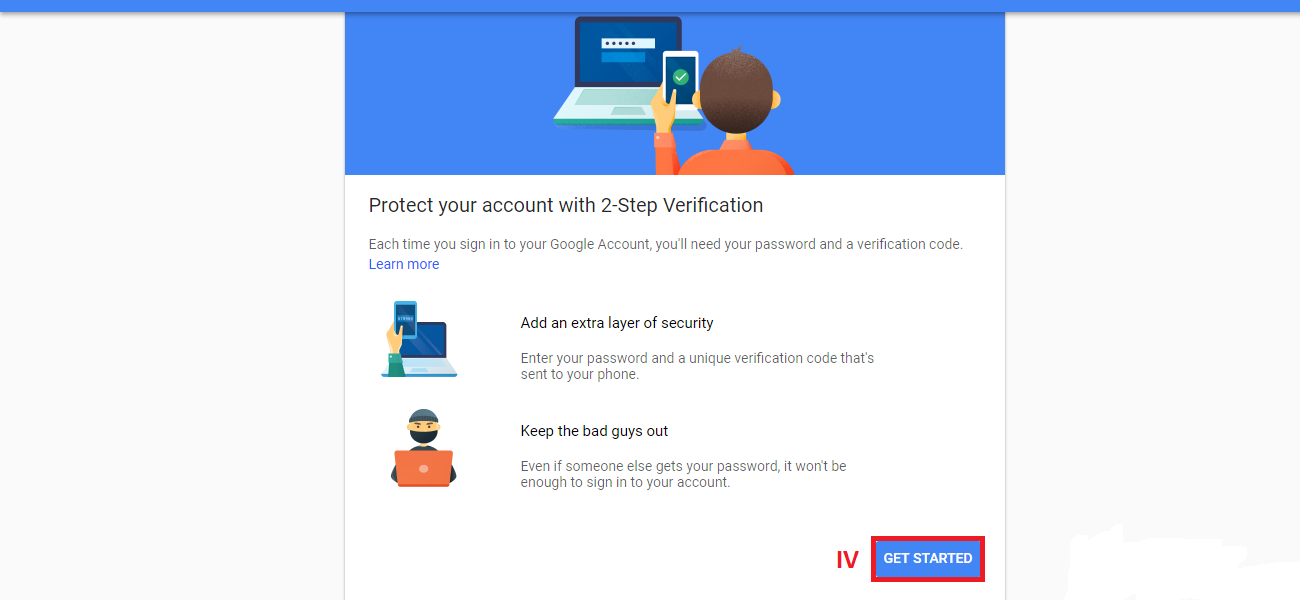
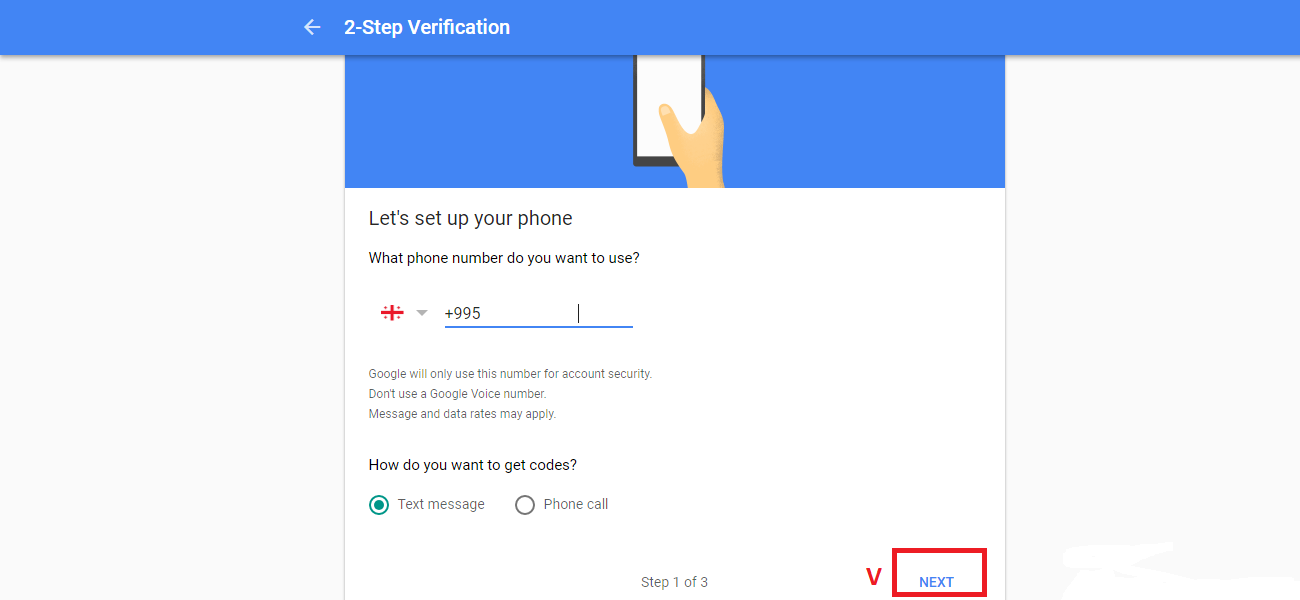
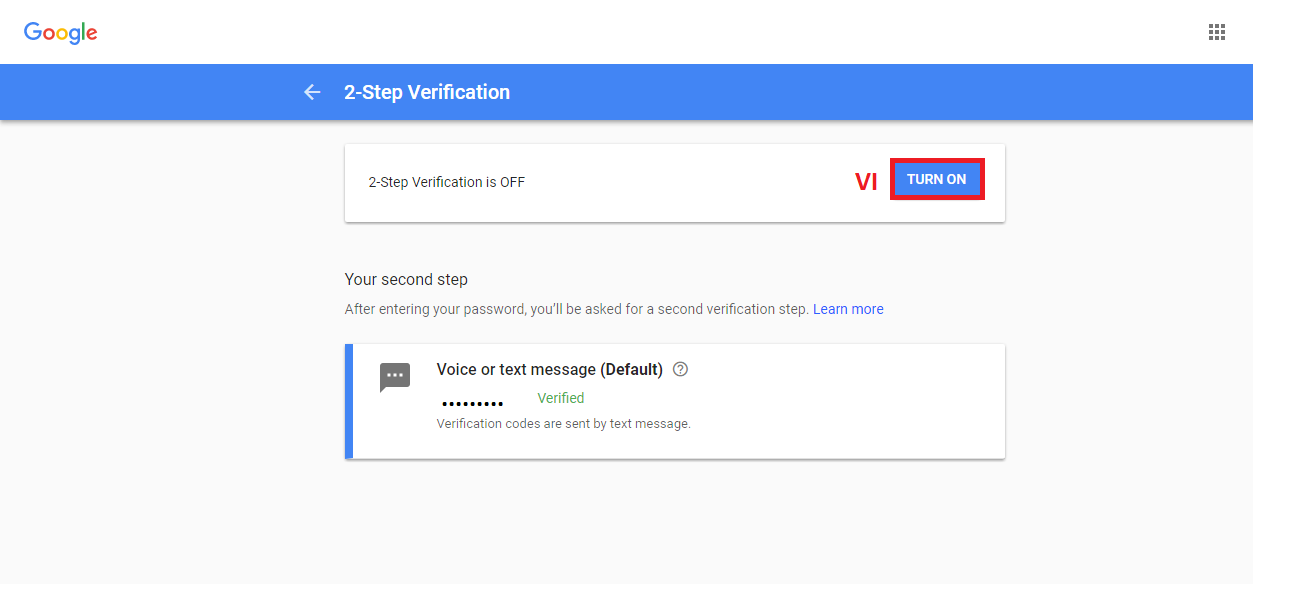
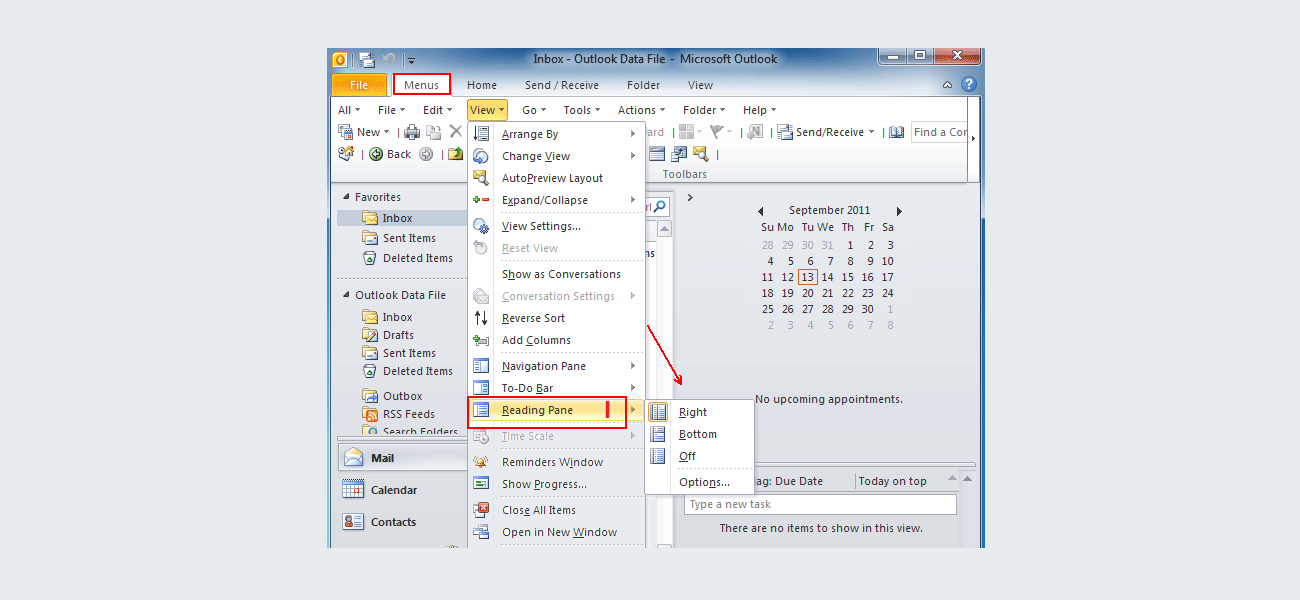
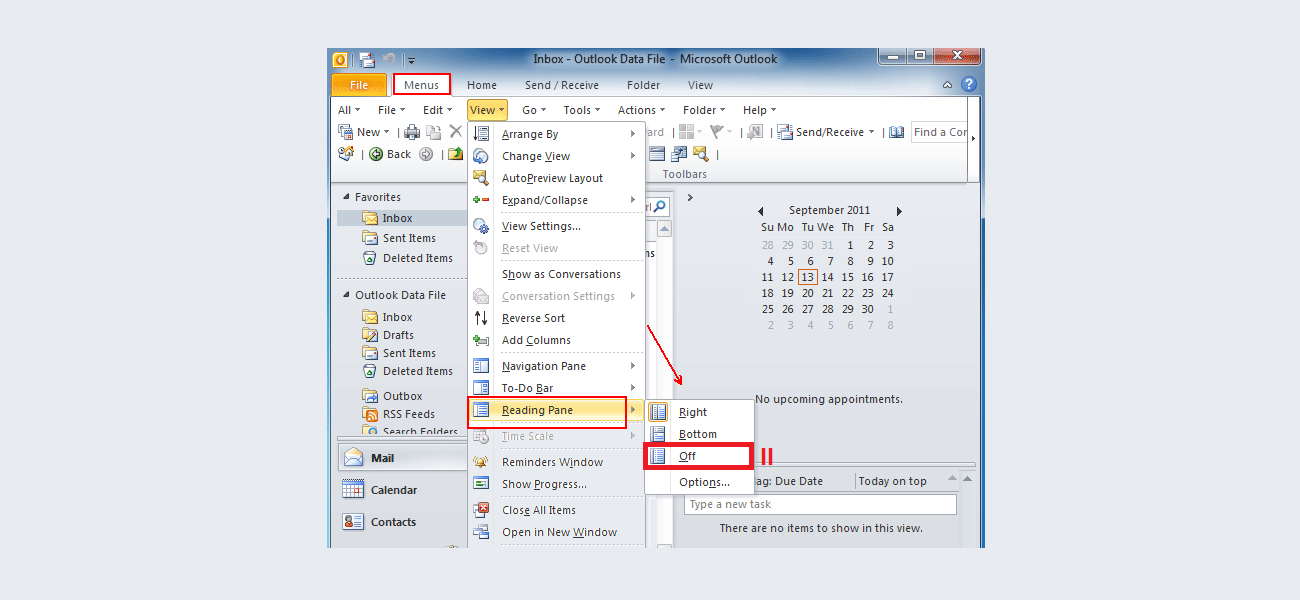
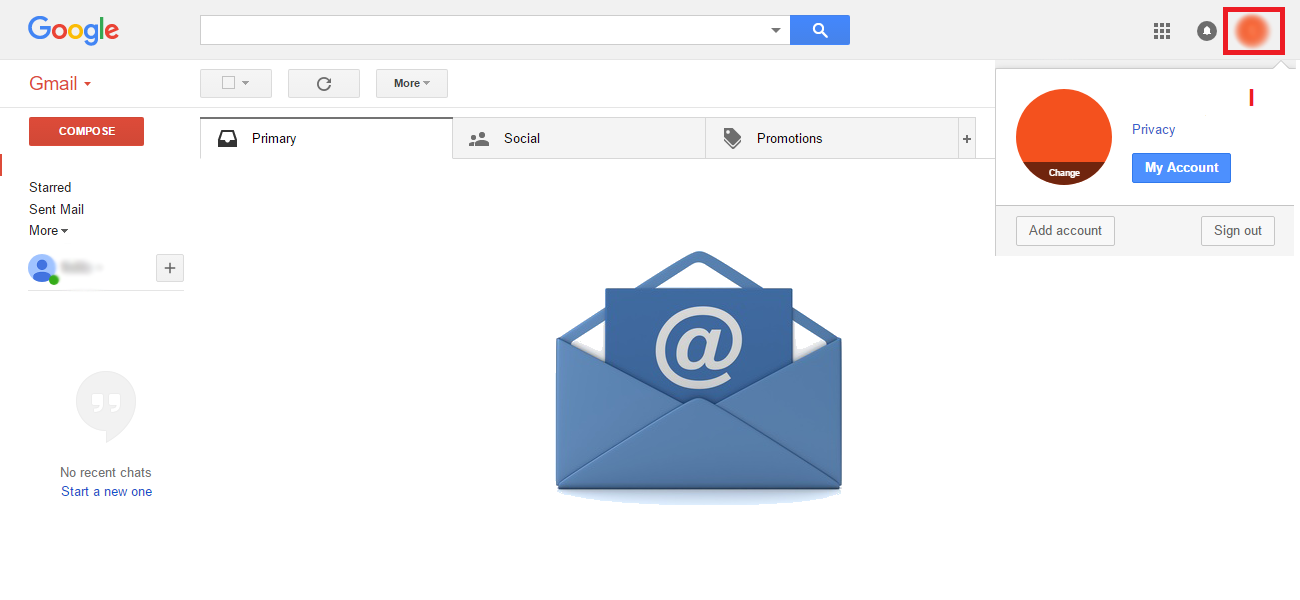
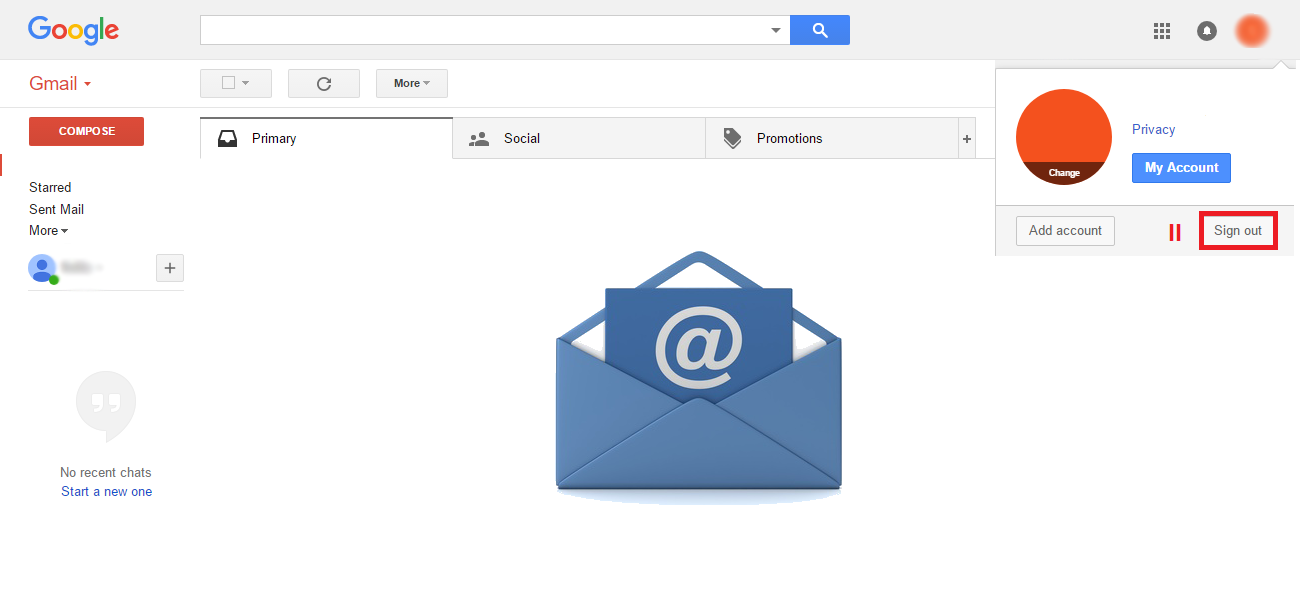
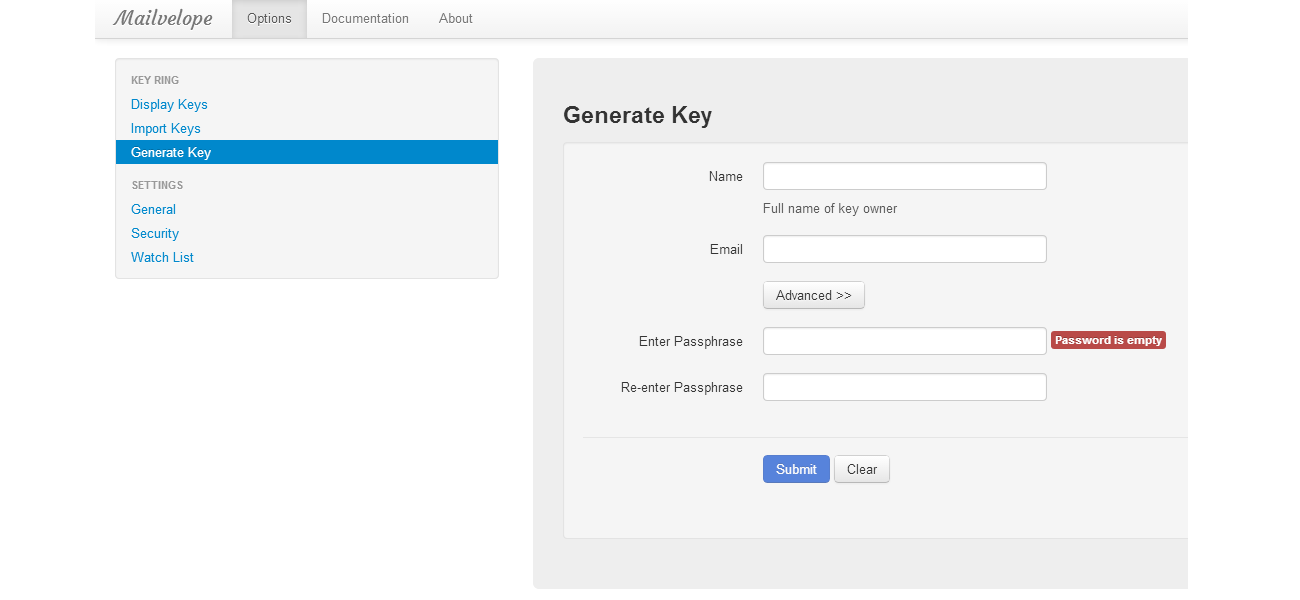
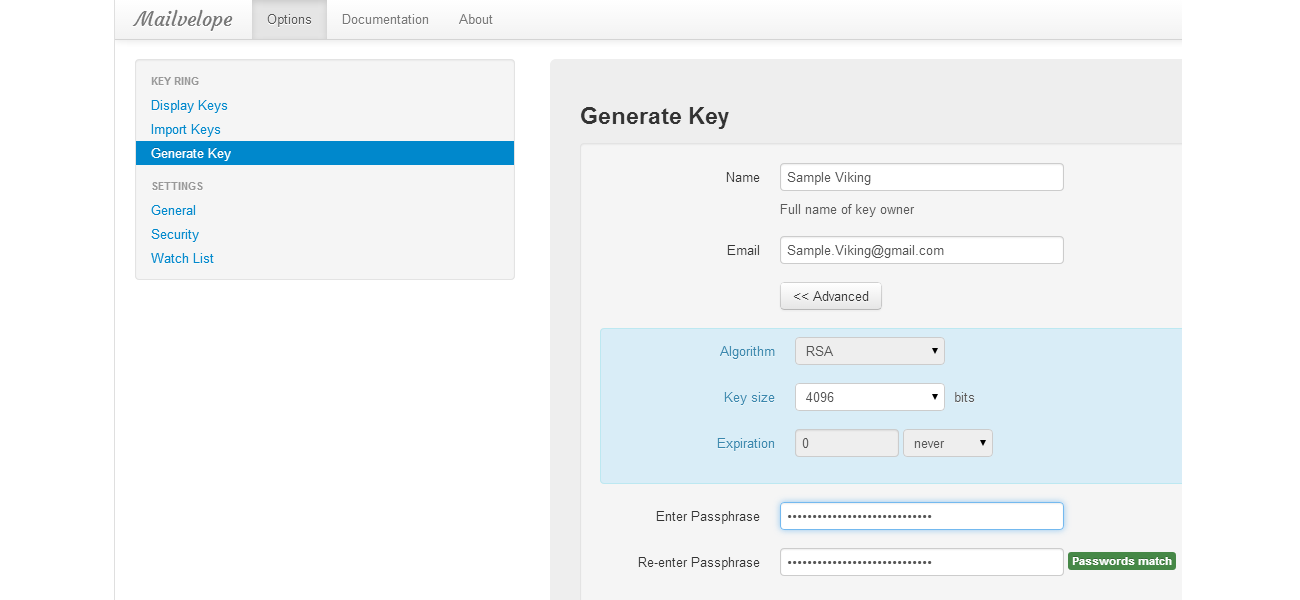
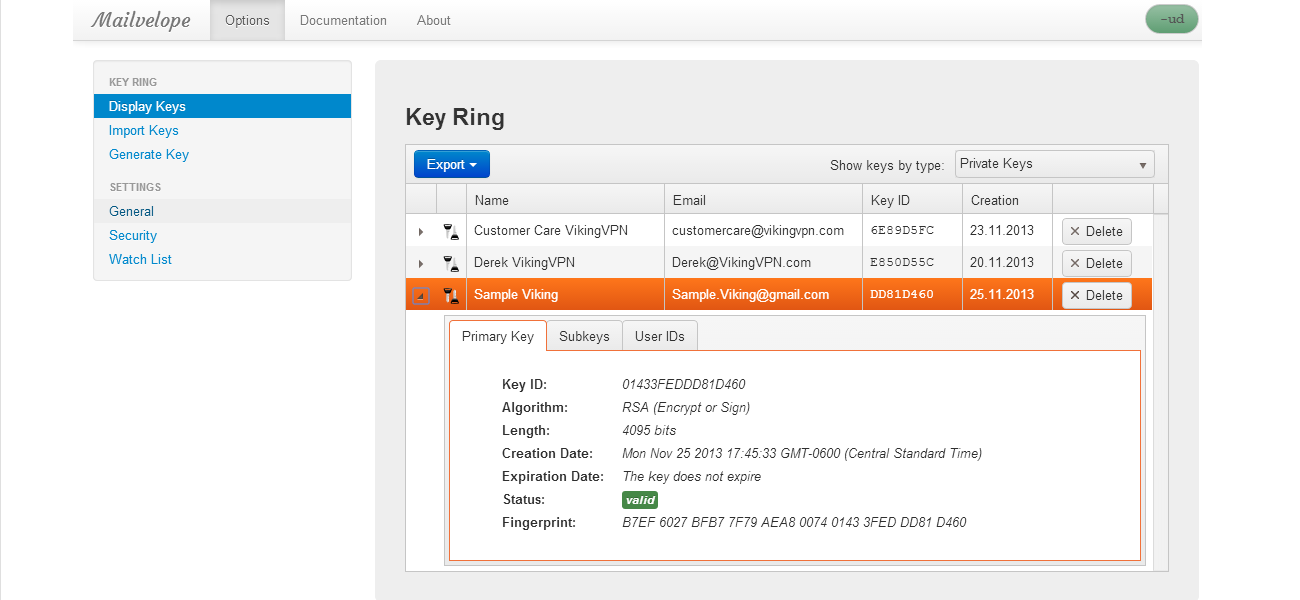
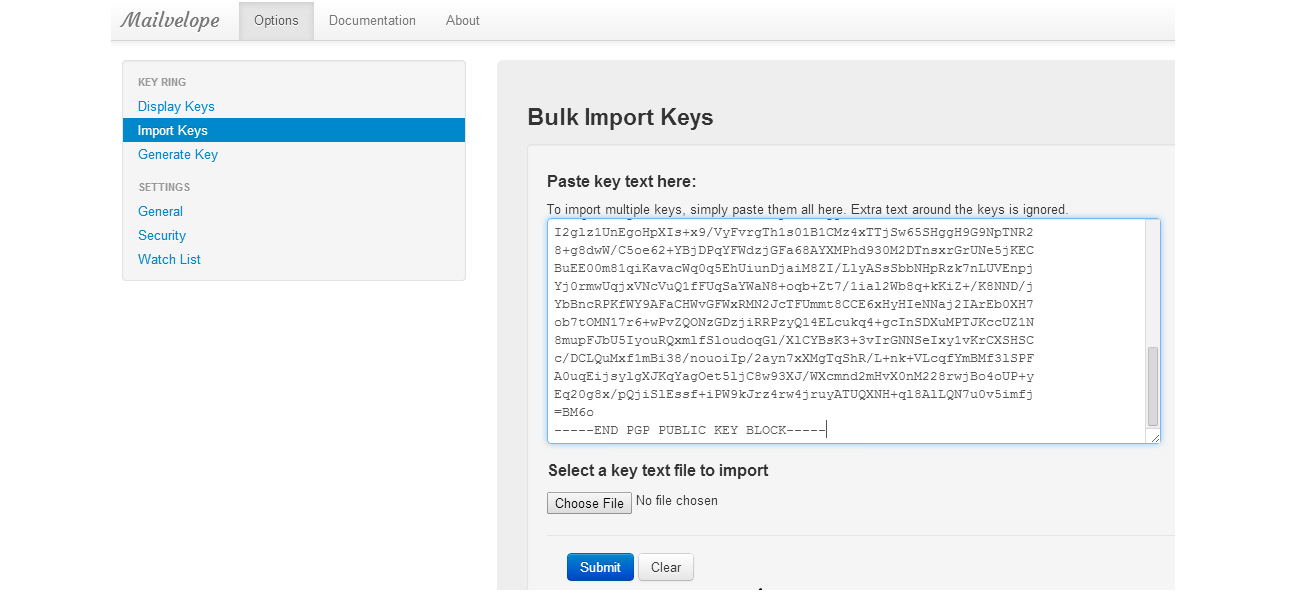
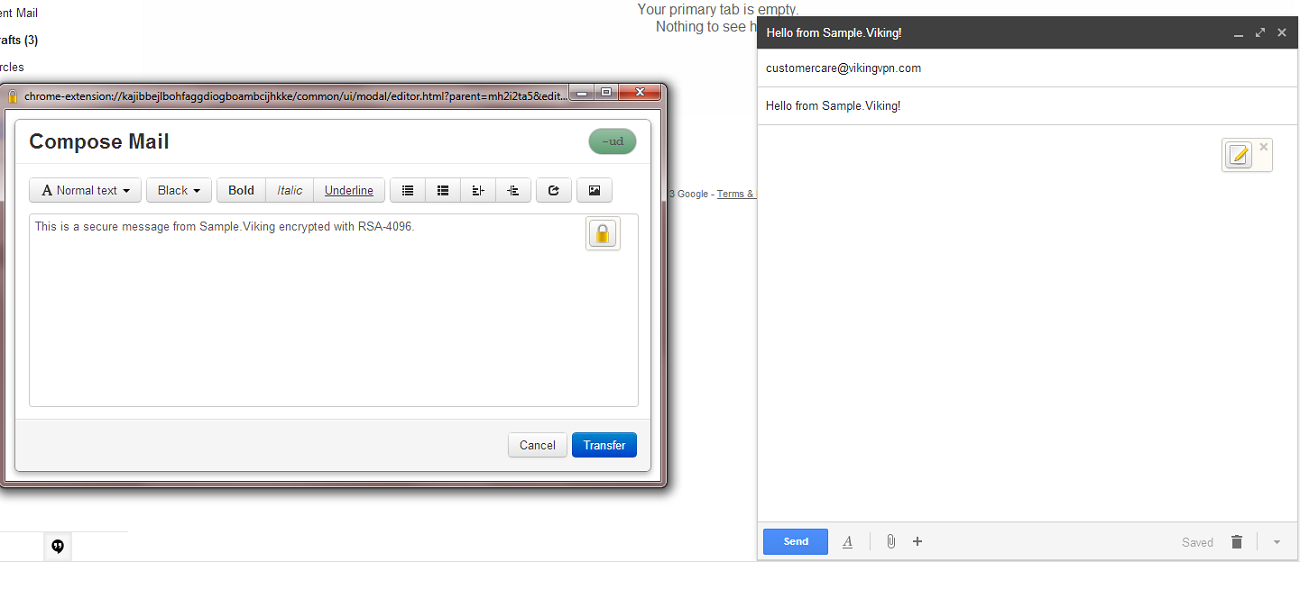
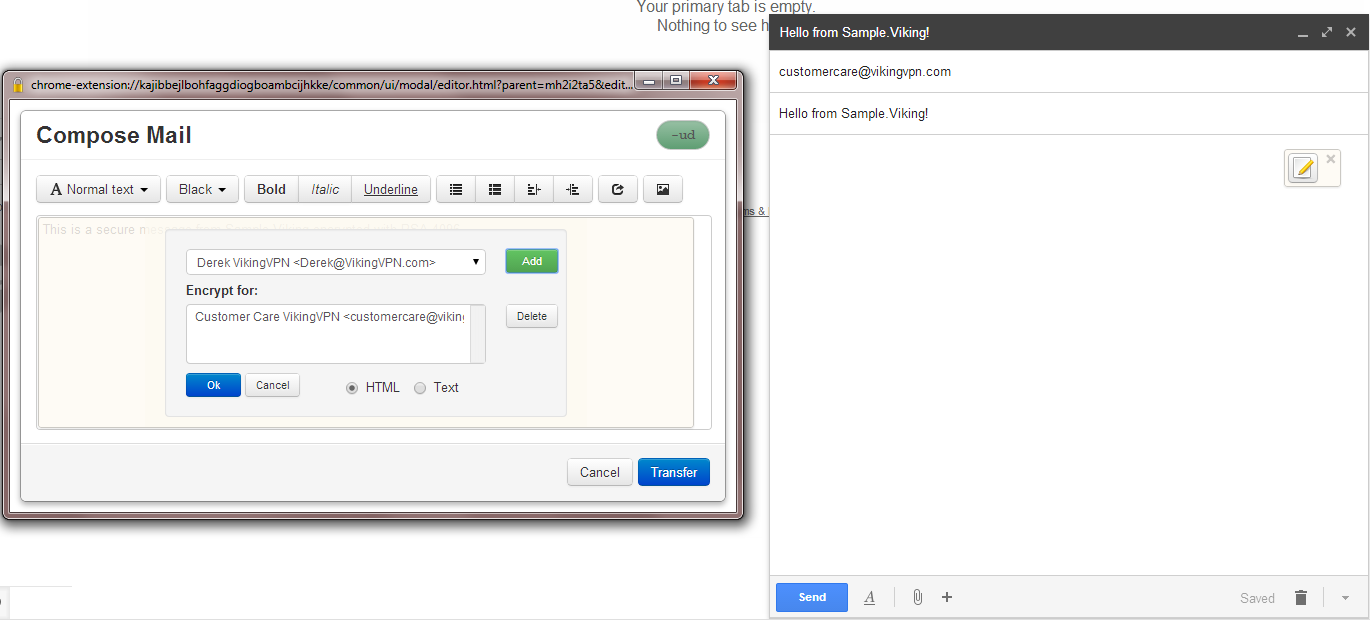
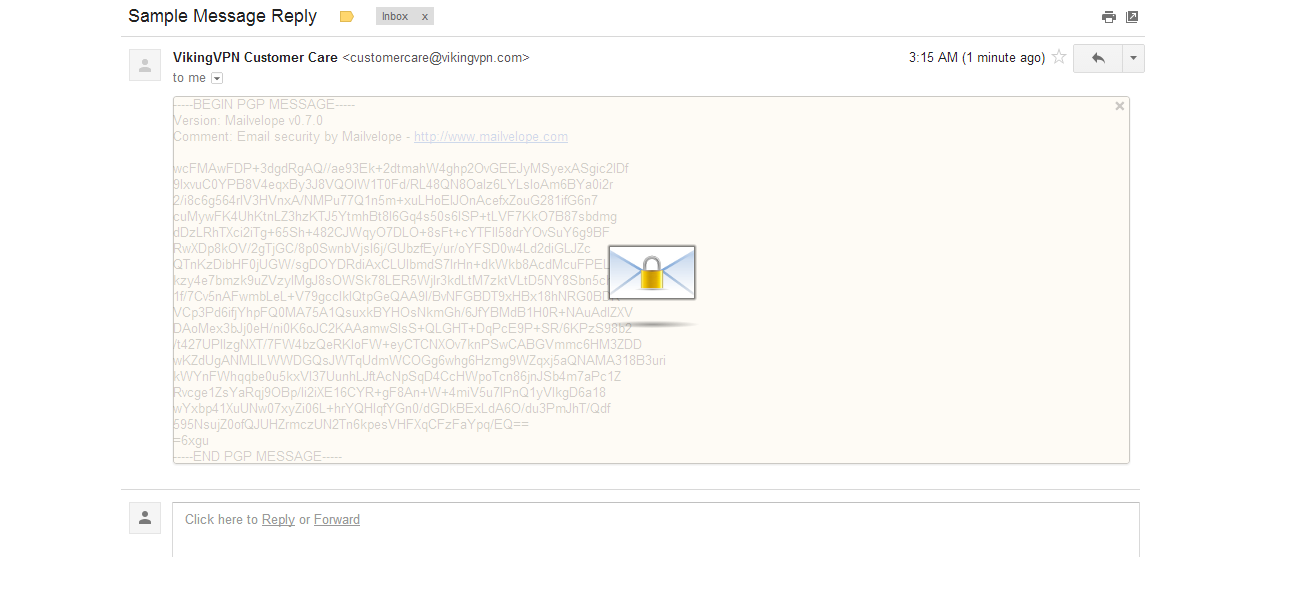
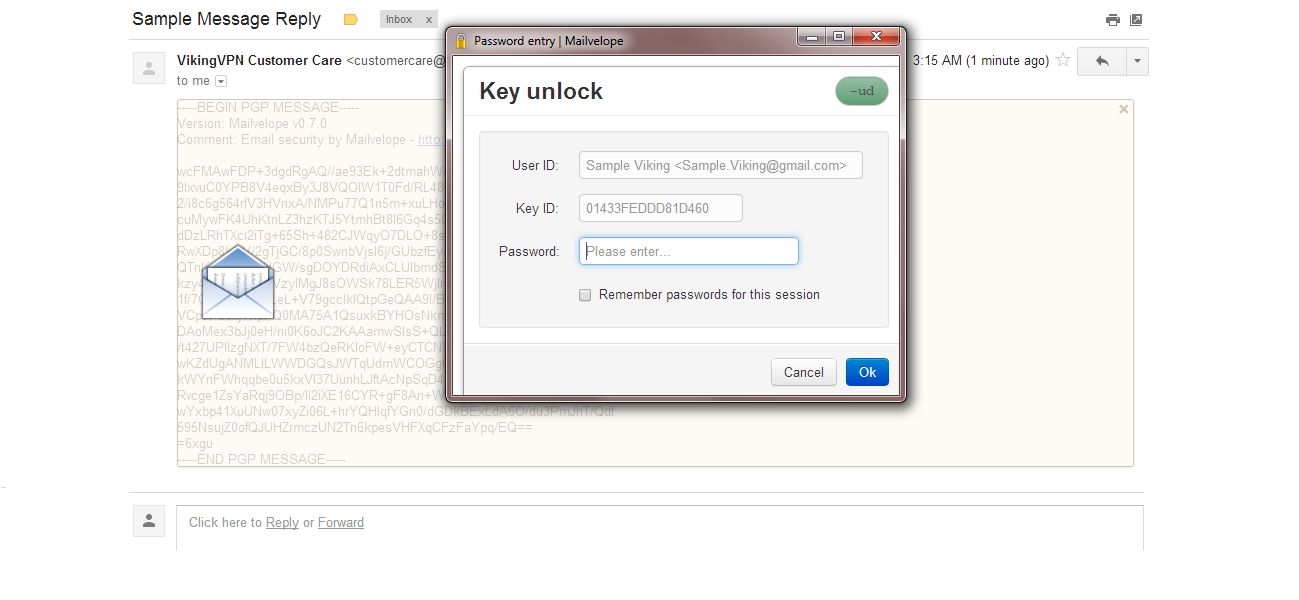
Even though it is impossible to completely negate the risk of cybercrime, there are ways to minimize it; ways offered by e-mail service companies themselves: