


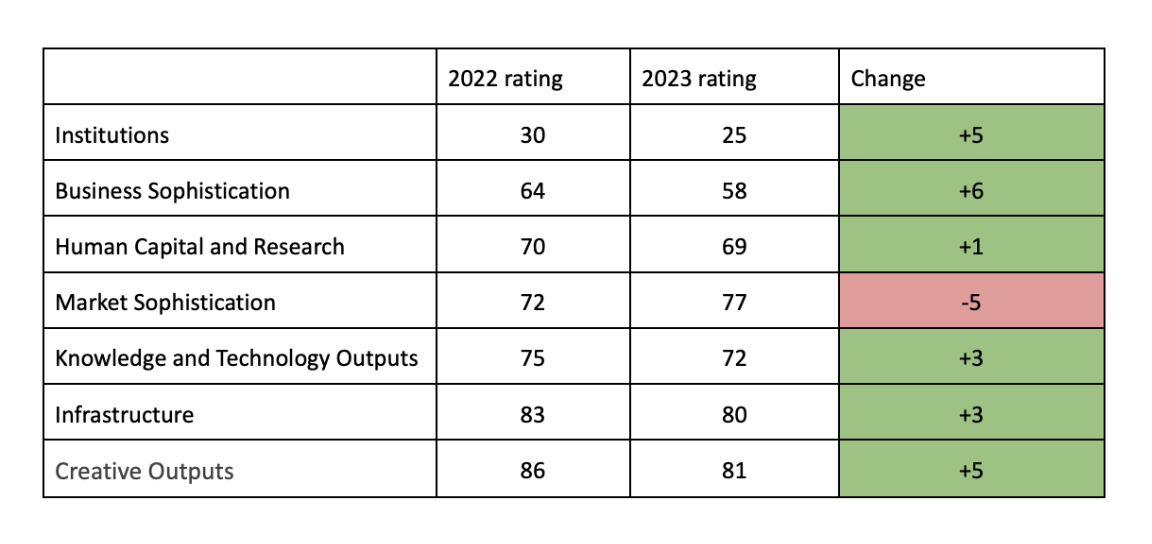
According to the 2023 results of the Global Innovation Index (GII), the rating of Georgia improved by 9 positions compared to the 2022 result, rising from the 74th spot to the 65th spot. However, despite a noticeable advancement in its position, the country received one of the lowest scores in recent years (29.9), only surpassing the record low score of 2022 (27.9).
The Global Innovation Index (GII) assesses 132 countries on innovation performance. The GII aims at a comprehensive analysis of innovation, taking into account innovation inputs and outputs. The assessment is based on up to 80 indicators around 7 thematic categories.
Assessment categories:
- Institutions (Institutional environment, Regulatory environment, Business environment);
- Human Capital and Research (Education, Research and development (R&D));
- Infrastructure (Information and communication technologies (ICTs), General infrastructure, Ecological sustainability);
- Market Sophistication (Credit, Investment, Trade, diversification and market scale);
- Business Sophistication (Knowledge workers, Innovation linkages, Knowledge absorption);
- Knowledge and Technology Outputs (Knowledge creation, Knowledge impact, Knowledge diffusion);
- Creative Outputs (Intangible assets, Creative goods and services, Online creativity).
The Index report presents country results both in terms of economic groups (high-income, upper middle-income, lower middle-income, and low-income countries) and according to regional groups. Within the framework of the Index, Georgia is considered an upper middle-income country. In the 2023 edition, Georgia showed high results in only 3 categories out of the 7. Namely, Institutions, Human Capital, and Business Sophistication received above-average scores. In the previous year, Georgia received a similar assessment in only two categories. However, in the remaining four categories - Market Sophistication, Infrastructure, Knowledge and Technology Outputs, and Creative Outputs - the country received a below-average score. According to these results, Georgia is in the 14th spot among the 33 upper middle-income countries. In this group of countries, China, Thailand, Brazil, North Macedonia, South Africa, Moldova, Jamaica, and Jordan stand out in terms of innovation development.
As for the regional aspect, Georgia belongs to the group of West Asia and North Africa, which includes countries like the United Arab Emirates, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkey, Cyprus, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Tunisia, etc. In the region, Georgia is in the 8th spot out of 18 countries, which marks a 3-spot improvement compared to the previous edition. Similar to the previous year’s results, Georgia received above-average scores only in the Institutions category, receiving below-average scores for the region in the remaining 6.
In 2023, Georgia’s score improved in five components - Market Sophistication, Human Capital and Research, Business Sophistication, Knowledge and Technology Outputs, and Creative Outputs. A regression was observed in 2 components - Institutions and Infrastructure. Despite minor progress, the country still has a low score (29.9) in the Global Innovation Index. However, it should be noted that according to the 2023 results, the country advanced 9 positions in the global rating, which was due to methodological changes in the Index. It should also be noted that a number of countries that were ahead of Georgia in the 2022 rating received scores lower than Georgia in the 2023 assessment, such as, for example, Peru, which in 2022 was in the 65th spot with a score of 29.1 but fell to the 76th spot with a score of 27.1 in 2023. A similar trend was observed in the cases of Tunisia (from 73th spot (27.9 score) to the 79th spot (26.9)), Bosnia and Herzegovina (from 70th spot (28.5 score) to the 77th spot (27.1)), and several other countries.
GII 2023 differs from previous years in that the pandemic and post-pandemic years contain a large volume of data. 88% of the data covers the years 2020-2023. The integration of such a large volume of data, consideration of the specific contexts of the countries, different approaches resulting from the pandemic, and the War in Ukraine had a large impact on the 2023 rating. It is therefore important to consider these factors when analyzing the 2023 GII rating.
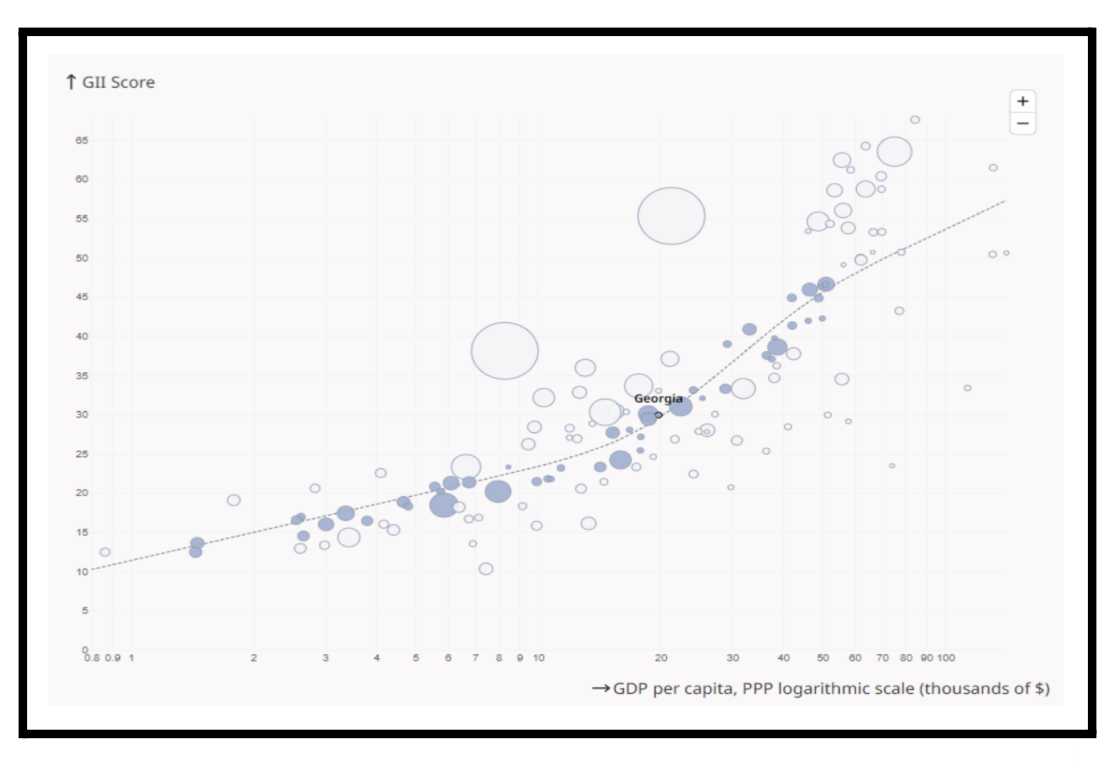
By observing Georgia’s indicators, the Index found positive trends in the correlation between the country’s GDP and innovativeness. The graph below presents countries in terms of GDP (per capita) and the innovation indicator (GII score). The trendline reflects the average expected innovation indicator according to the economic performance of a country. The countries above the trendline showed results higher than average, while those below it have an innovation indicator that lags behind their development level. In terms of Georgia’s results, the trend is still positive.
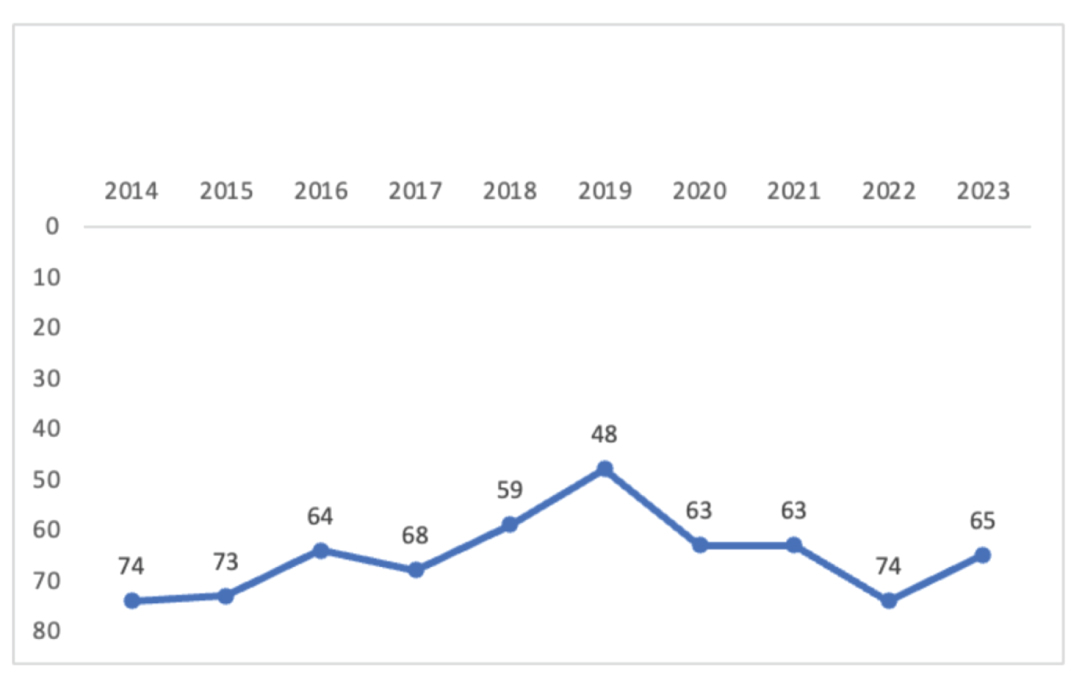
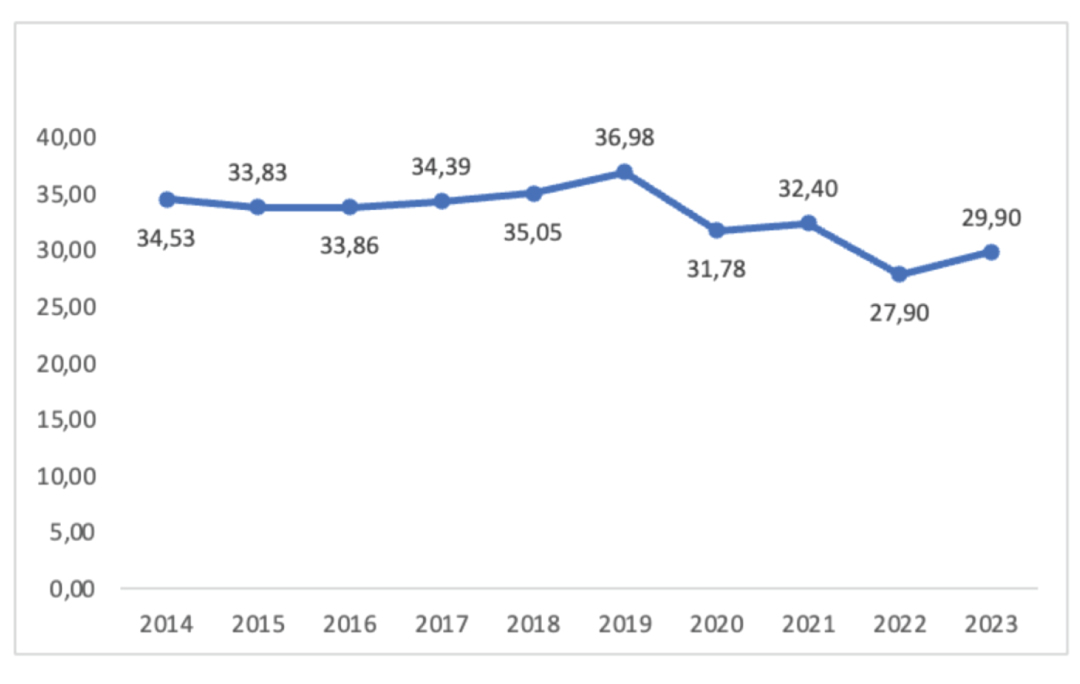
Georgia had the highest position in the rating (48th place) with the highest score (36.88) in the GII rating in 2019. The result worsened significantly during the pandemic and post-pandemic periods. In 2020-2021, the country’s position fell to the 63th place, while in 2022 it stood at 74. This is related, on the one hand, with the pandemic, and on the other hand, with changes in the GII methodology. Since the pandemic, an improvement in the position was seen in 2023, when the country reached the 65th spot, although, as noted above, the change in the rating is related to methodological amendments and other independent factors. The country still has a fairly low score in a number of categories and lags significantly behind its pre-pandemic (2019) result.
Georgia's ranking by year
Georgia's score by year
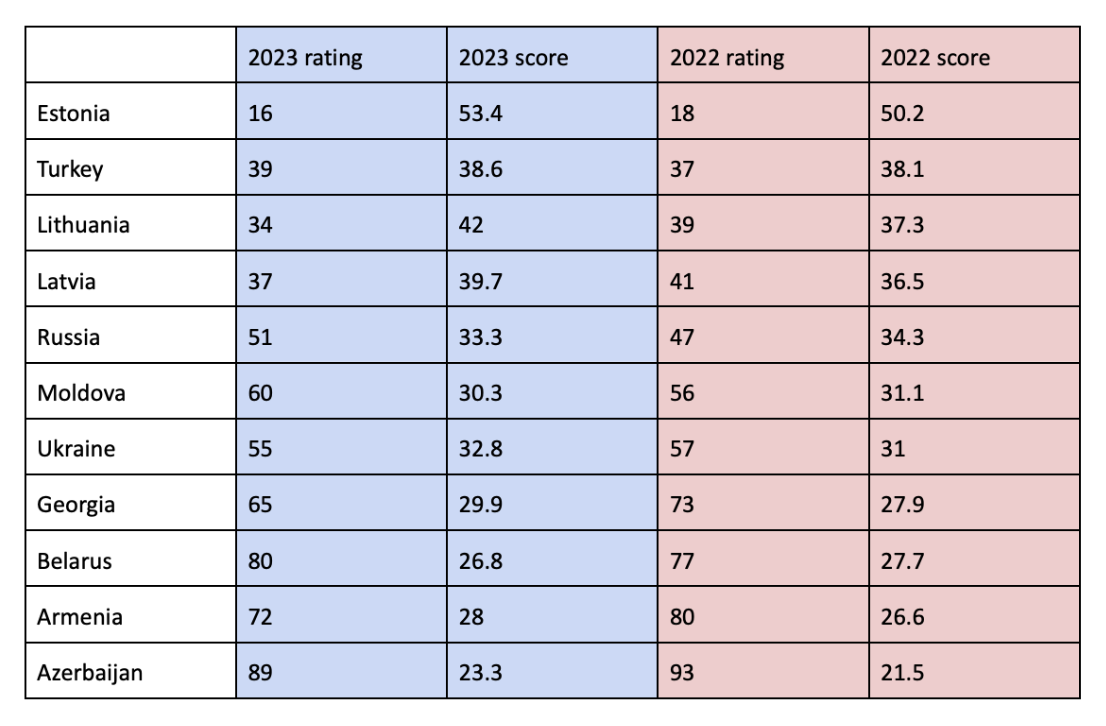
Comparison with Other Countries in the Region (Neighboring, Eastern Partnership, and the Baltics)
Georgia is still ahead of its neighbors (except for Russia) in the rating, but is significantly behind the rest. Specifically, according to the 2023 results, among the 11 neighboring, Eastern Partnership, and Baltic countries Georgia is in the eighth spot and is ahead of only Belarus, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. It should be noted that according to the 2019 results, Russia, Ukraine, and Georgia are in the 46th, 47th, and 48th spots, respectively, but since then Russia and Ukraine’s results have seen significant improvement, unlike Georgia, and due to this the gap between these countries has been growing every year.
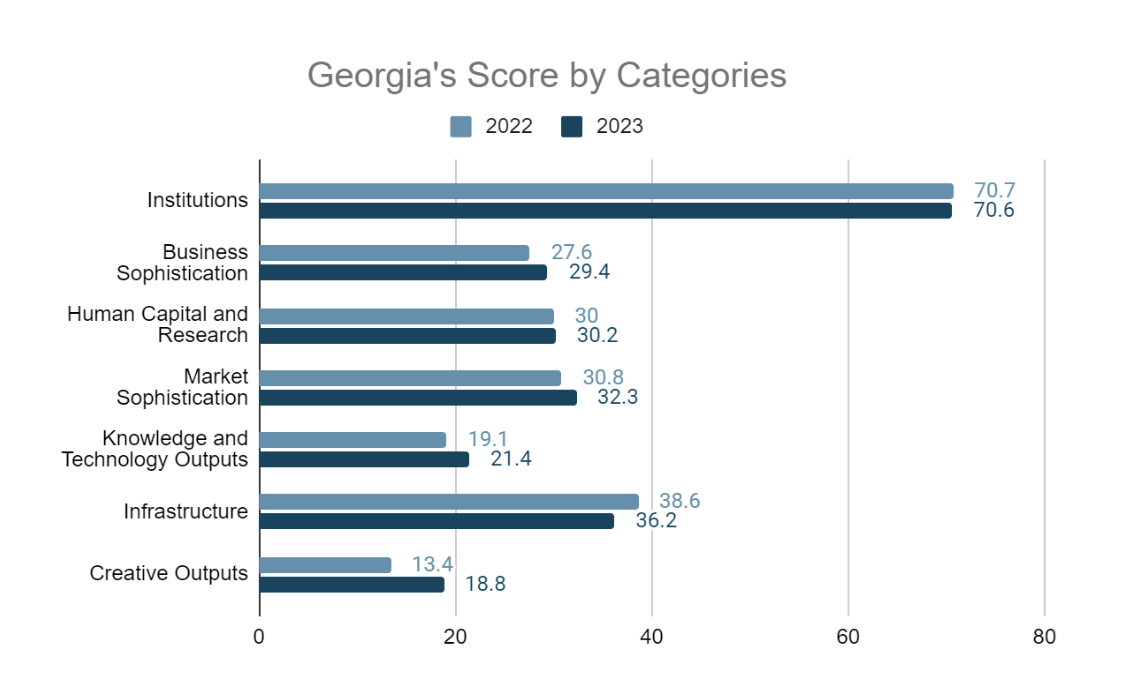
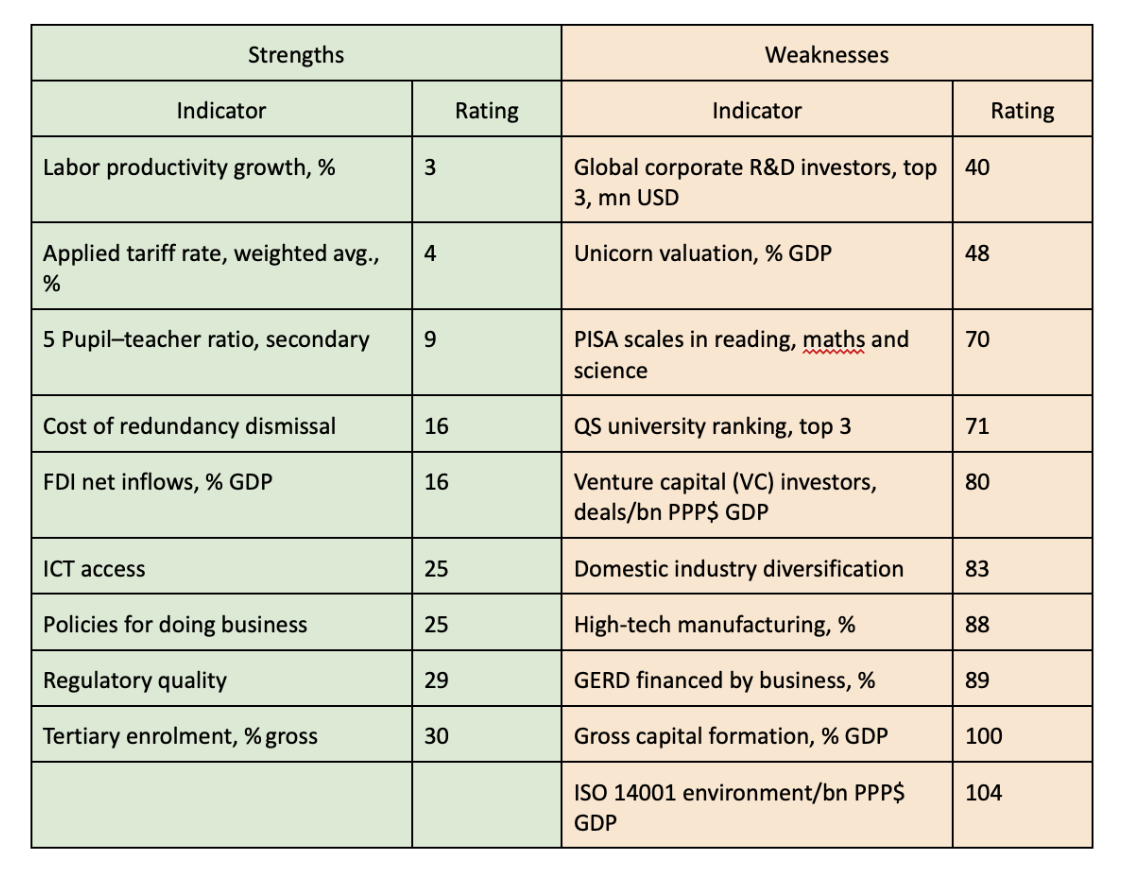
The Index revealed Georgia’s strong and weak points in terms of innovation through specific indicators. The country holds a leading position in one of the indicators of the Knowledge and Technology category, which measures labor productivity growth. In the category of Market Sophistication, the applied tariff rate was evaluated quite positively; The country scored highly in a Human Capital indicator that measures the ratio of students to teachers in the country. In the same category, the rate of matriculation into higher education institutions was also evaluated positively. The only indicator in Infrastructure that received a high score was access to information and communication technologies. Similarly, only one indicator in the Business Sophistication - foreign direct investment net inflows as a percentage of GDP - was assessed positively. The Institutions category should be highlighted, where Georgia received relatively high scores in 3 out of 7 indicators - regulatory quality, policies for doing business, and cost of redundancy dismissal.
As for deficiencies, students have a low performance in PISA scales in reading, maths, and science, and there is a lack of universities with high ratings, which speaks to a low-quality education system. In the same category, the country received a low score in the global corporate R&D investors indicator. In terms of Business Sophistication, Georgia has a weak performance in research and development spending by businesses, which may indicate the passivity of the private sector in R&D. The country is behind in the rating in terms of a number of financial indicators, which, together with the above-mentioned weaknesses, is reflected in the low share of high-tech production.
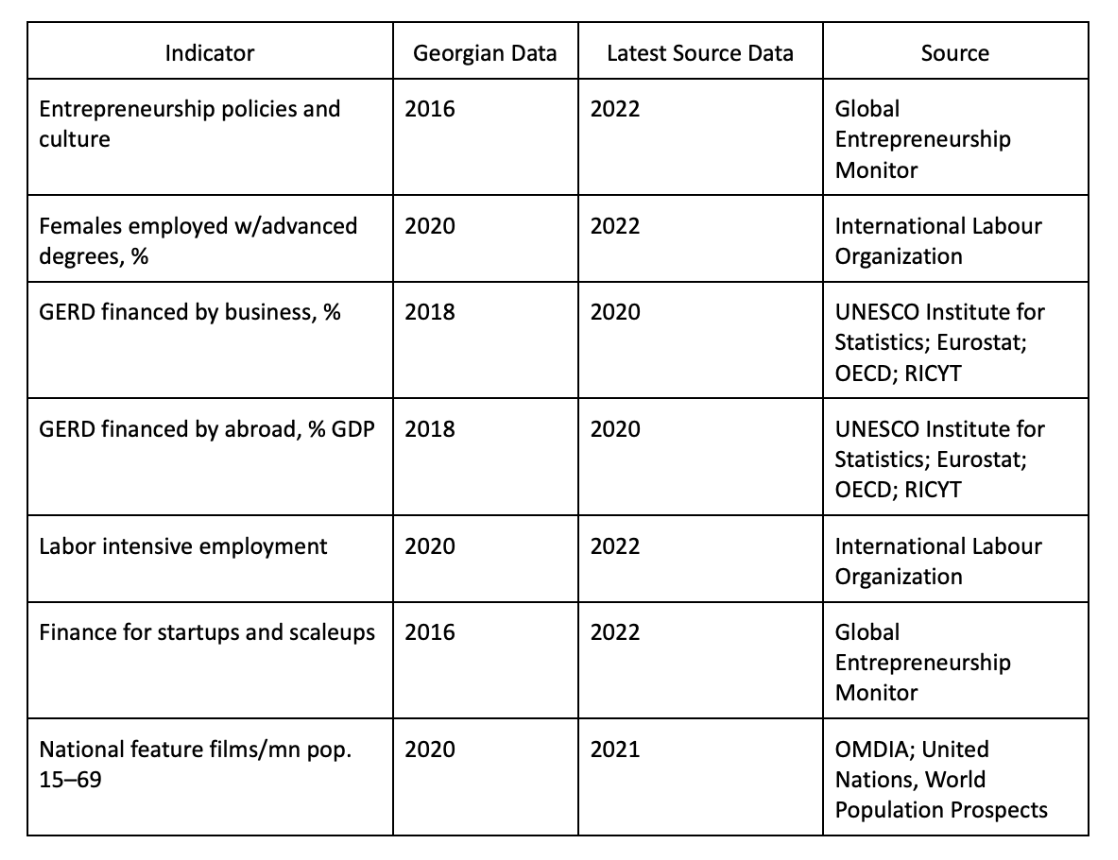
The GII Index uses a variety of sources, international indices, and reports for the assessment of specific indicators. The table presents the sources that did not include an assessment of Georgia, pointing to a need for the country to be more involved and produce data in these directions. Public agencies as well as non-governmental and academic institutions can collaborate with these sources. For example, The UNESCO Institute for Statistics cooperates with national statistical agencies, ministries, and other statistical agencies. Meanwhile, the Global Monitor of Entrepreneurship (GME) relies primarily on partnerships with leading academic institutions.
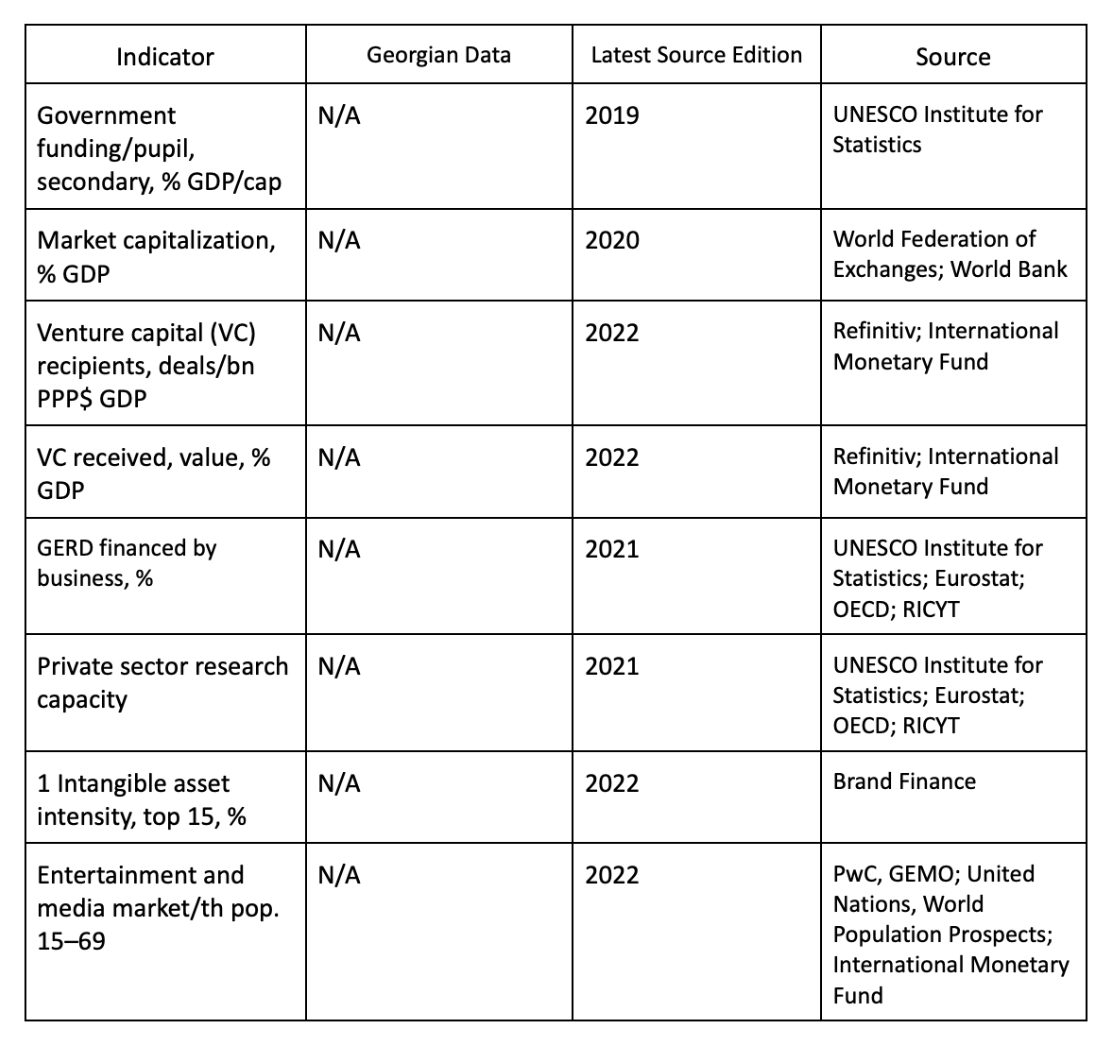
It should be noted that in 2022 Georgia did not have any data on two additional indicators - policies for doing business and finance for startups. The country produced statistics on these topics for 2023.
The indicators that were evaluated in the past, but need to be updated should also be highlighted:
The GII Index used a very large volume of data to assess countries during this year - data from both the pandemic and post-pandemic periods, thereby showing a wider picture of the development of countries in this direction. While Georgia saw a significant improvement in its position in the global rating according to 2023 results, as well as an improvement in its position in relation to other countries in the region, it still received one of the lowest overall assessment scores in recent years and did not exceed the best results achieved in 2019, which points to a stagnation of policies that would facilitate innovation in previous years, especially against the background of other countries.
The 2023 Georgia results of the Global Innovation Index show stagnation in terms of economic and innovative development in specific areas. Innovative capabilities play an important role in the development of the economy, and therefore a complex and comprehensive approach to the challenges in this sector and elimination of gaps is necessary, especially in the field of education. It is also important to establish a financing structure for innovative startups both from the state side and through the interest and attraction of the so-called risk capital (venture capital).
Specific indicators for which data could not be collected should also be taken into account. It is important to deepen collaboration with the sources mentioned above and to update outdated data.