


In 2021, the Georgian economy surpassed the 2019 level by 3%, despite significant growth in foreign debt and high inflation. In 2020, the Covid-19 Pandemic had a negative impact on economic growth, in Georgia and in other countries. Despite the -6.8% decline in 2020, GDP increased by 3% in 2021 compared to 2019. External debt Increased by GEL 10.5 billion (+ 50%) in the last two years. Total inflation exceeded 15% in the same period. Georgia's economy is expected to grow by 6% in 2022[1]. This does not significantly exceed the US (5.2%) and EU (4.2%) averages.
In 2021, the highest economic growth (11%) as compared to 2019 was recorded in Turkey, compared to the region and neighboring countries. The inflation rate in 2021, meanwhile, was 17% in the country. The Pandemic and war had an adverse effect on Azerbaijan's economy, resulting in -1.4% economic downturn in 2021 as compared to 2019.
A significant increase in inflationary pressure was caused by increased access to financial resources and the encouragement of aggregate demand, among other external factors in 2021. Despite the high economic growth, the average annual inflation rate in Georgia reached 10% in 2021. With this indicator, Georgia is in second place after Turkey (17%) in the region. It should be noted that the exchange rate in Turkey depreciated by 23% against the US dollar, while in Georgia - only by 4%, in the same period.
Graph 1: Economic Growth and Inflation (%) by Country
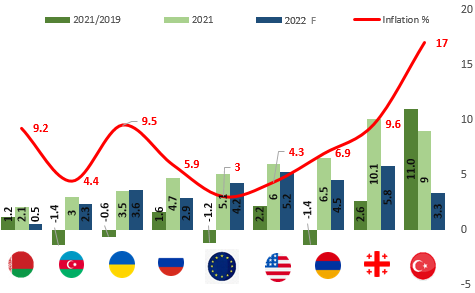
Source: IMF, Geostat, IDFI
The high growth of issued loans significantly impacted economic growth in 2021. Loans issued to the economy increased by 13% and reached GEL 42 bln in 2021. Specifically, household loans increased by 15%, approx. up to GEL 22 bln, and business loans increased by 11% up to GEL 20 bln in 2021. In total, the share of issued loans to GDP was 70% at the end of 2021.
Graph 2: Increase in monthly issued household and business loans in 2021, compared to January
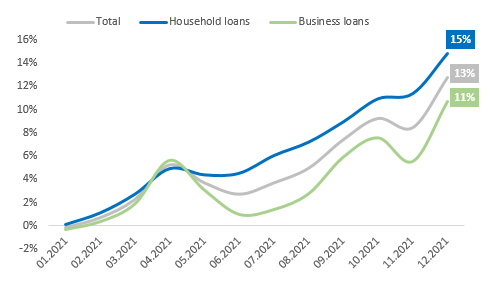
Source: The National Bank of Georgia, IDFI
In the first three quarters of 2021, wholesale and retail trade and manufacturing have the highest shares in GDP, with 16% and 11%, respectively. The share of real estate activities decreased by 1.8 P.P compared to the previous year and resulted in 10% in the same period. The share of agriculture reduced significantly by -1.3 P.P. compared to the previous year. This was caused by the growth of other sectors, however.
Graph 3: Sectorial structure of GDP in 2021 and change compared to 2020 (three quarters)
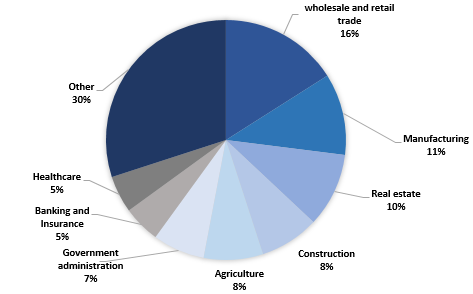
Source: Geostat, IDFI
Tax revenues have been rising mainly due to the high inflation rate over the past two years, as the economy grew only by 3% in this period. Tax revenues increased by 17% YoY and reached GEL 9.5 bln in the three quarters of 2021. The increase was -4.7% YoY in the corresponding period in 2020. This was a result of tax delays according to the COVID-19 anti-crisis plan and economic slowdown.
Graph 4: Tax revenues in the consolidated budget (bln GEL)
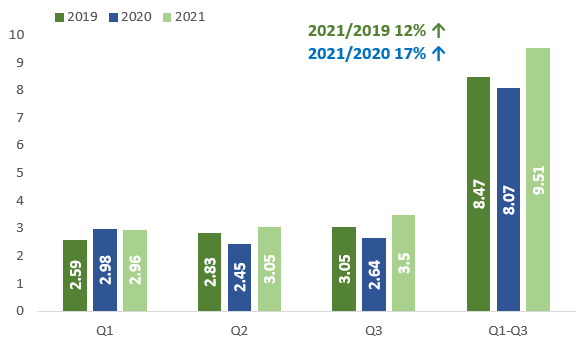
Source: Geostat, IDFI
In 2020, the ratio of government debt to GDP reached a record high - 63%. In 2021, the ratio is still high at 53%, which is -10 P.P. lower than the rate in 2020. This was caused by maintaining a stable exchange rate and economic growth. Armenia has the highest debt-to-GDP ratio (62%), while Russia has the lowest rate (18%) in the region.
Graph 5: Government Debt to GDP ratio, by Country (%)
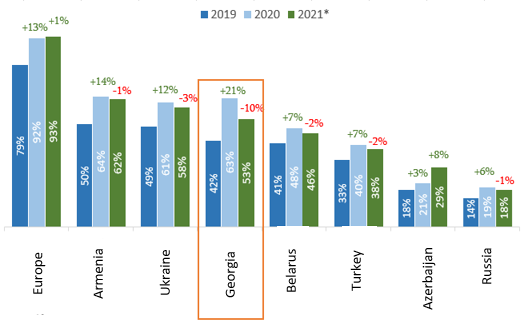
Source: MOF, Statista, Trading Economics, IDFI
*Forecasted numbers for 2021
-----
[1] International Monetary Fund (IMF) forecast

This material has been financed by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency, Sida. Responsibility for the content rests entirely with the creator. Sida does not necessarily share the expressed views and interpretations.